Figure 2.
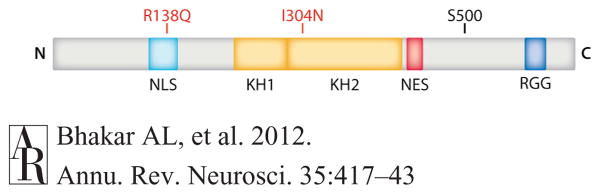
Functional domains of FMRP. Human FMRP, a 632 amino acid polypeptide (gray bar), has a nuclear localization signal (NLS; light blue), two K-homology domains (KH1 and KH2; orange), an RGG (arginine-glycine-glycine) box (dark blue), and a nuclear export sequence (NES; red). R138Q and I304N are naturally occurring mutations in patients with developmental delay and a severe form of FX, respectively. I304N abolishes polyribosome association. S500 is a major site of phosphorylation. Abbreviations: N, amino terminus; C, carboxy terminus; FMRP, fragile x mental retardation protein.
