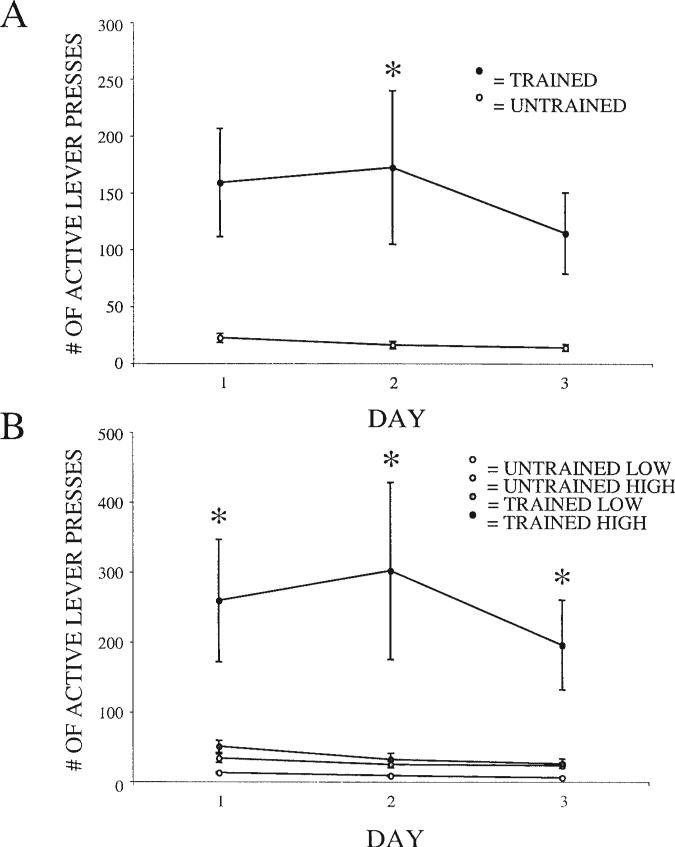
Figure 6.
A: Active lever presses in trained (n = 25) and untrained (n = 15) rats during the first 3 days of cocaine access. Analysis of variance demonstrated a significant main effect for group ( p = .002), and post hoc tests revealed a significant difference between groups on Day 2. *p < .05. B: Cocaine self-administration median split from trained (n = 25) and untrained (n = 15) rats. High = high cocaine self-administration; low = low cocaine self-administration. Analysis of variance demonstrated a significant main effect for group ( p < .001), and post hoc tests showed the trained high group to be significantly different from all other groups. *p < .01. Error bars represent standard error.