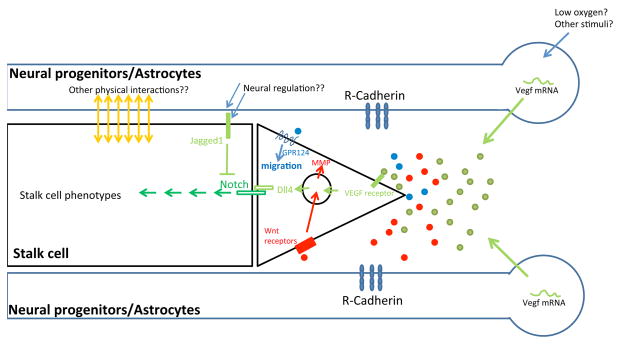
Figure 1. Neural regulation of initial vessel ingression.
The blue rectangles on the top and bottom represent radial glia fibers or astrocytic processes, while the circles to the right represent cell bodies of neural progenitor cells or astrocytes. The black rectangle and triangle in the middle represent endothelial stalk and tip cells, respectively. R-Cadherin from neural cells potentially stabilizes filopodia from tip cells. Low oxygen levels or other stimuli may up-regulate Vegf gene expression within neural cells. Secreted VEGF proteins (green dots) then induce endothelial Dll4 expression, which is critical for tip cell selection and stalk cell development. Other Notch ligand such as Jagged1 has opposite functions to Dll4, suggesting that a balance between Dll4 and Jagged1 may determine tip cell number. Neural progenitor cells also secrete Wnt ligands (red dots), which stimulate endothelial cell migration probably by up-regulating MMP levels. Unidentified diffusible factors (blue dots) from neural cells may bind to GPR124 on endothelial cells to regulate Cdc42-dependent cell migration (in the forebrain).