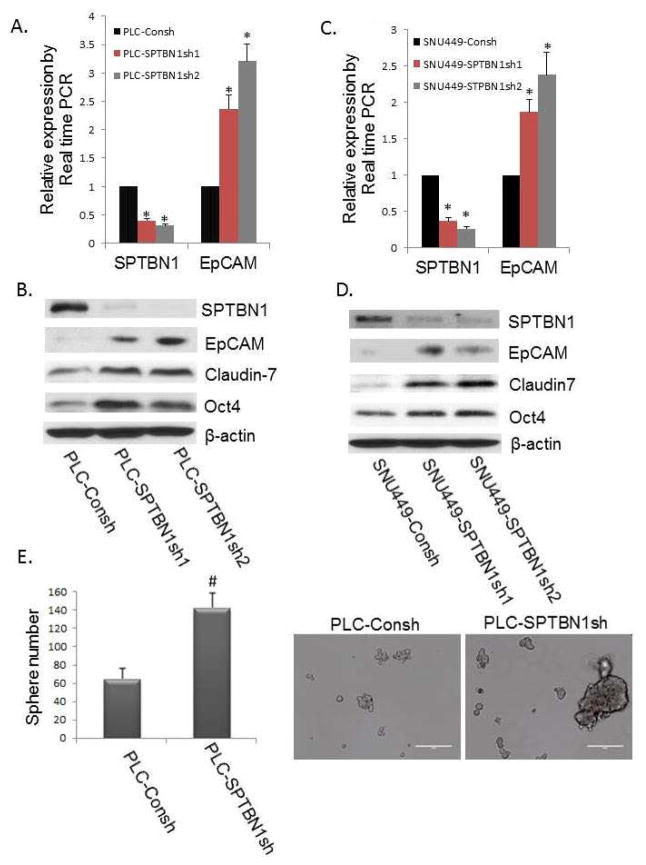
Figure 2.
Reduction of SPTBN1 promotes stem cell like traits in the PLC/PRF/5 and SNU449 HCC cell lines. A and C: Comparison of the EpCAM mRNA levels by real time PCR in the two HCC cell lines with stable knockdown of SPTBN1 expression generated with two different shRNA constructs (indicated by SPTBN1sh1 and SPTBN1sh2) compared with control cells carrying the shRNA control vector (indicated by Consh) in which there is no knockdown of SPTBN1. The left sides of Figure 2A and 2C show decreased SPTBN1 expression resulting from stable knockdown of the SPTBN1 gene in PLC/PRF/5 (A) or SNU449 cells (C) compared with the Consh shRNA containing control cells. The right panels illustrate increased EpCAM expression in HCC cells in SPTBN1 knockdown cells compared with control cells (*P<0.01). B and D: Western Blot of stem/progenitor cell markers, including EpCAM, Claudin7, and Oct4 in PLC/PRF/5 cells (B) and SNU449 cells (D) without or with stable knockdown of SPTBN1 expression. E. Inhibition of SPTBN1 expression in PLC/PRF/5 cells (carrying stable SPTBN1 shRNA knockdown constructs) promoted sphere formation compared with control cells (PLC-Consh). Twice as many spheres (size of sphere >100 μM) and an increased number of larger spheres (size of sphere > 200 μM) were formed by SPTBN1 knockdown PLC/PRF/5 cells as compared to unaltered cell lines carrying only control PLC-Consh (P<0.05).