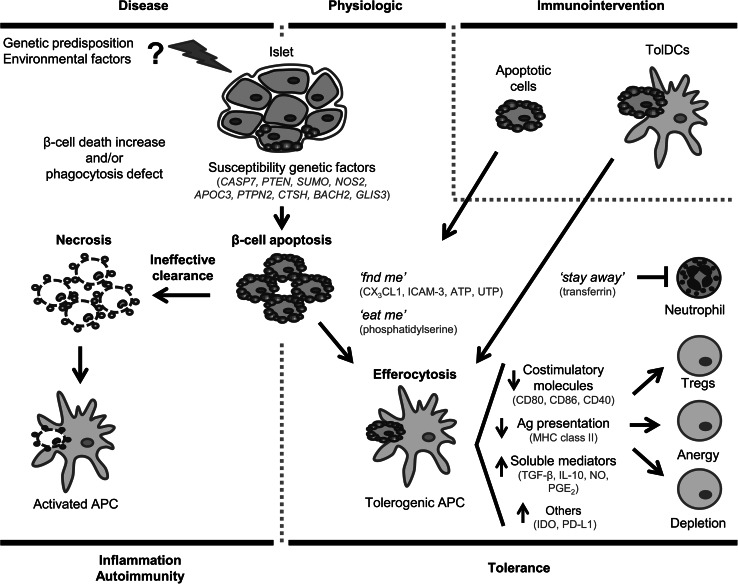
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of β-cells apoptosis and efferocytosis in type 1 diabetes. β-cells that undergo apoptosis are recognized and phagocytosed by APCs, leading to physiologic tolerance induction. However, an increase in the rate of β-cells apoptosis rate and/or defects in efferocytosis result in the activation of APCs, contributing to inflammation, to the lack of tolerance to self and to autoimmune disease. Strategies of immunointervention based on apoptosis, such as apoptotic cell administration or tolDCs-pulsed with apoptotic β-cells- could help to the reestablishment of immunological tolerance to β-cells autoantigens, lost in type 1 diabetes