Abstract
Erythromycin A released peptidyl-tRNA in the in vitro polypeptide synthesis system with bacterial components programmed by synthetic polynucleotide. This is consistent with our hypothesis that erythromycin A inhibits translocation by preventing proper situation of oligopeptidyl-tRNA in the donor (D) site on ribosomes.
Full text
PDF
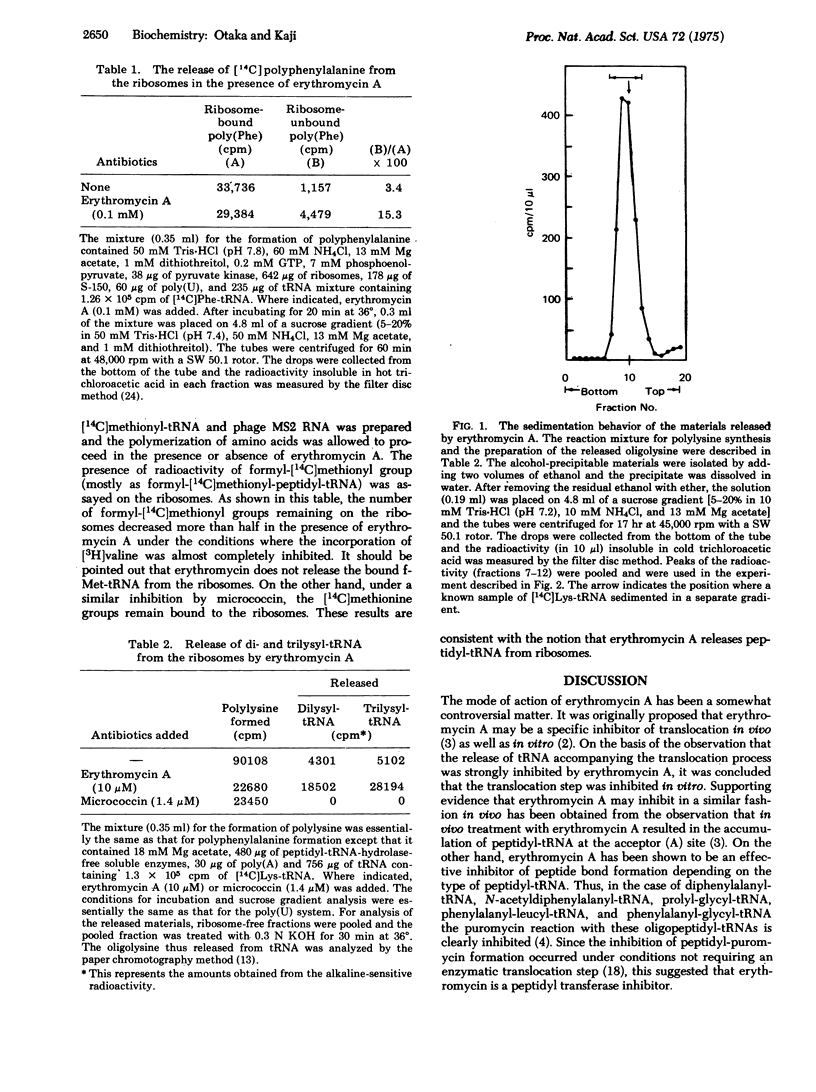
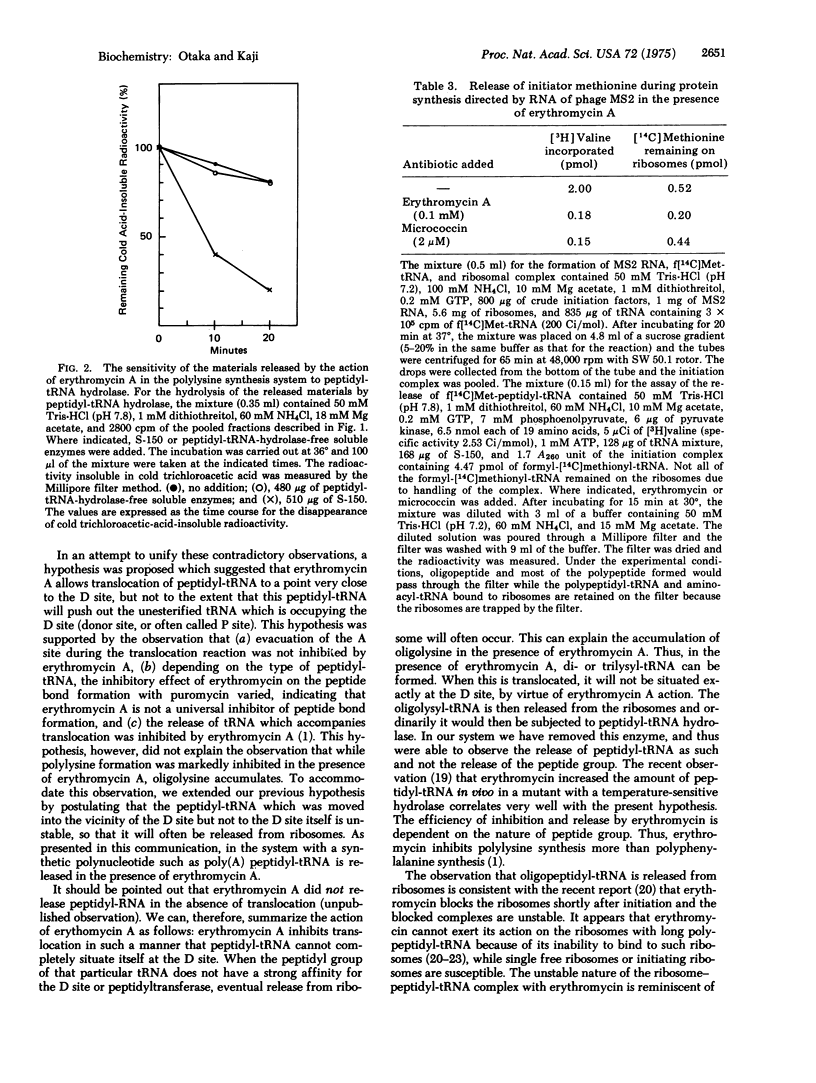

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anaka K., Teraoka H. Effect of erythromycin on polylysine synthesis directed by polyadenylic acid in an Escherichia coli cell-free system. J Biochem. 1968 Nov;64(5):635–648. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., McQuillen K. Bacterial protein synthesis: the effects of antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuzin F., Kretchmer N., Greenberg R. E., Hurwitz R., Chapeville F. Enzymatic hydrolysis of N-substituted aminoacyl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2079–2086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groot N., Groner Y., Lapidot Y. Peptidyl-tRNA. VII. Substrate specificity of peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 20;186(2):286–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima A., Kaji A. Factor-dependent release of ribosomes from messenger RNA. Requirement for two heat-stable factors. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;65(1):43–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90490-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima A., Kaji A. Role of elongation factor G and a protein factor on the release of ribosomes from messenger ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7580–7587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishitsuka H., Kaji A. Comparative studies on the mechanism of action of lincomycin, streptomycin, and erythromycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 22;37(3):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90943-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kössel H., RajBhandary U. L. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXXVI. Enzymic hydrolysis of N-acylaminoacyl-transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 14;35(3):539–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Putterman M. Accumulation in gram-postive and gram-negative bacteria as a mechanism of resistance to erythromycin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1111–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1111-1117.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E. Effects of macrolides on peptide-bond formation and translocation. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2054–2061. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E. Erythromycin, a peptidyltransferase effector. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4864–4872. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Davis B. D. Breakdown by streptomycin of initiation complexes formed on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1148–1155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka T., Kaji A. Evidence that fusidic acid inhibits the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the donor as well as the acceptor site of the ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):46–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka T., Kaji A. Micrococcin: acceptor-site-specific inhibitor of protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):101–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Antibiotics as probes of ribosome structure: binding of chloramphenicol and erythromycin to polyribosomes; effect of other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):255–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Wallace B. J., Davis B. D. Selective action of erythromycin on initiating ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4653–4659. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Teraoka H., Tamaki M. Peptidyl puromycin synthesis; effect of several antibiotics which act on 50 S ribosomal subunits. FEBS Lett. 1971 Feb 12;13(1):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80666-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Otaka T., Kaji A. Further studies on the mechanism of erythromycin action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 26;331(1):128–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Zamir A., Elson D. On the specificity and stability of an enzyme that hydrolyzes N-substituted aminoacyl-transfer RNA's. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):701–707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALEY S. G., WATSON J. The action of trypsin on polylysine. Biochem J. 1953 Sep;55(2):328–337. doi: 10.1042/bj0550328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot N., Panet A., Lapidot Y. Enzymatic hydrolysis of peptidyl-tRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Apr 5;31(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


