Figure 3. Proposed mechanism, how PTPN22 is involved in IBD pathogenesis.
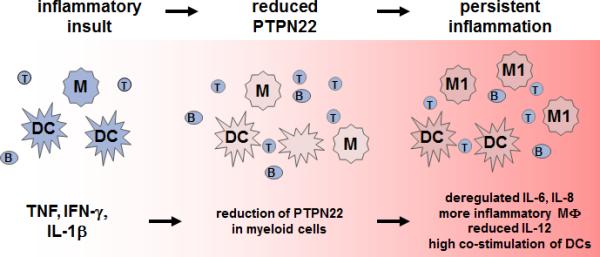
Inflammatory insults result in high levels of TNF, IFN-γ and IL-1β. TNF and IL-1β reduce PTPN22 expression in myeloid immune cells. Upon loss of PTPN22, monocytes/macrophages secrete increased levels of IL-6 and IL-8 and differentiate preferentially into pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages. The increased expression of co-stimulatory molecules on DC results in an enhanced activation of the adaptive immune system. B: B cell, DC: dendritic cell; IFN: interferon; M/MF: Macrophage; M1: inflammatory macrophage; T: T cell; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
