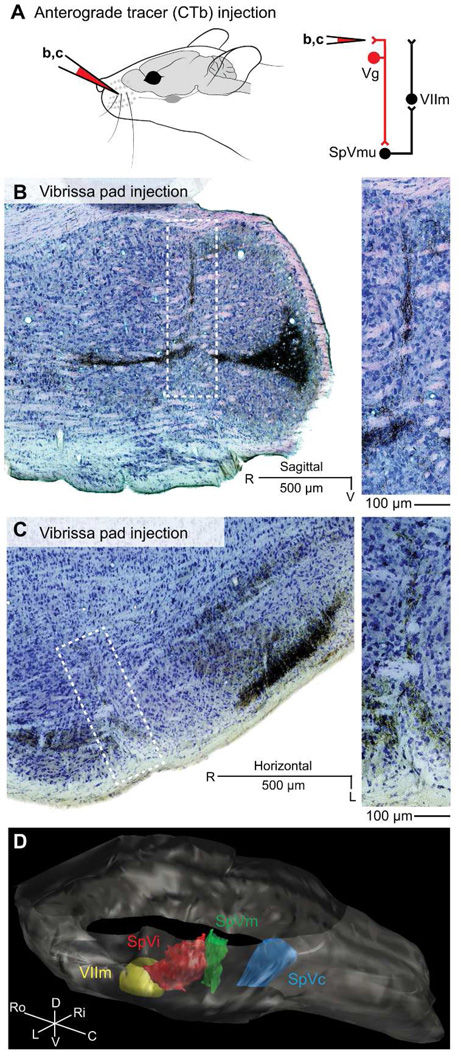
Figure 4. Trigeminal brainstem following focal injection of CTb into one or a few follicles of the mystacial pad.
A: Schematic of the location of cholera toxin B (CTb) injections. Red-colored connections in the circuit diagram indicate the projections under examination. Injections were performed in independent animals. B: Representative sagittal section. Dark product reaction against CTb reveals fine terminal structure of primary somatosensory inputs in trigeminal brainstem; Giemsa is used as a counterstain to cell bodies. Inset: Magnified portion of the border between SpVi and SpVc reveals a spatially localized peripheral termination zone of sensory inputs. C: Horizontal section, as in panel B. Spatially localized somatosensory inputs arborize on the border between nuclei SpVi and SpVc, in several laminar divisions of nucleus SpVc, and in part of the barrelette field of nucleus SpVi. D: Representative volumetric reconstruction of brainstem from the same data set shown in panel C, showing axonal innervation in trigeminal brainstem after focal CTb injection into mystacial pad. The view is from the left, caudal to and above bregma. For clarity, terminations rostral to SpVi are not shown.