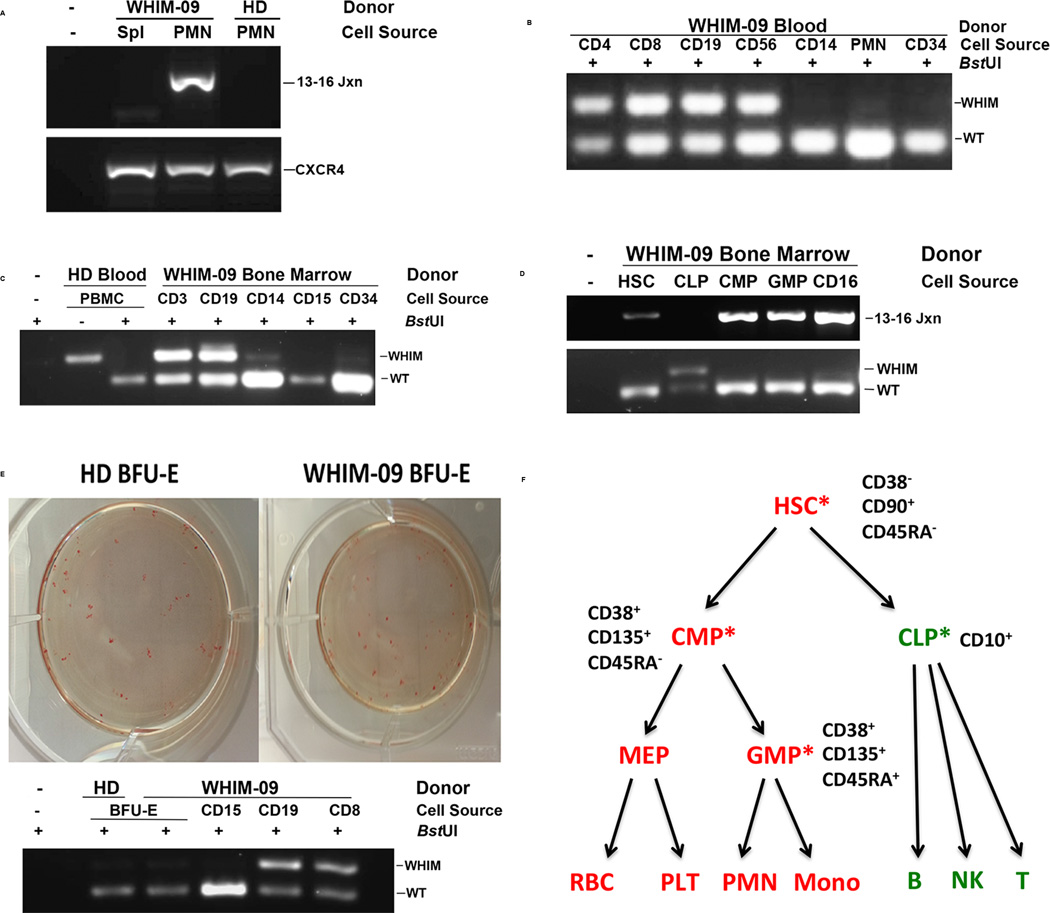
Figure 4. Chromothriptic CXCR4-haploinsufficient HSC replacement of the myeloid lineage, but not the lymphoid lineage, is associated with clinical remission in patient WHIM-09.
(A–E) Representative results from a BstUI PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism assay (BstUI), designed to distinguish the wild type CXCR4 allele (WT) from the CXCR4R334X WHIM allele (WHIM), as well as from a PCR assay specific for the chromothriptic chromosome (13–16 Jxn). PCR was performed on DNA obtained from the indicated donor leukocyte subsets purified either from blood using magnetic bead purification (B, E) or from a bone marrow aspirate using flow cytometric sorting (C, D). DNA was also prepared from archived WHIM-09 spleen and compared with peripheral blood PMN DNA (A), as well as from Burst-forming Unit-Erythroid colonies and compared with blood leukocyte subsets (E). WHIM-09, index patient; HD, healthy donor; Spl, spleen; PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocytes; 13–16 Jxn, PCR product specific for the chromothriptic junction between segments 13 and 16 of the chromothriptic chromosome of patient WHIM-09; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; CD4, purified CD4+ T cells; CD8, purified CD8+ T cells; CD19 purified CD19+ B cells; CD56, purified CD56+ natural killer cells; CD14, purified CD14+ monocytes; CD34, purified CD34+ hematopoietic cells; CD3, purified CD3+ T cells; CD15, purified CD15+ neutrophils; CD16, purified CD16+ neutrophils; HSC, hematopoietic stem cells; CLP, common lymphoid precursor; CMP, common myeloid precursor; GMP, granulocyte/monocyte precursor MEP, megakaryocyte-erythroid precursor; BFU-E, Burst-forming Unit-Erythroid; CXCR4, CXCR4 amplicon not digested with BstUI. (F) Summary of myeloid/lymphoid mosaicism for CXCR4R334X in patient WHIM-09. The immunophenotype used to purify each cell type from enriched CD34+CD45+ cells is summarized next to each cell type shown. Red, positive for CXCR4R334X; green, negative for CXCR4R334X; asterisks, purified cell types directly analyzed by PCR-RFLP for the WHIM mutation.