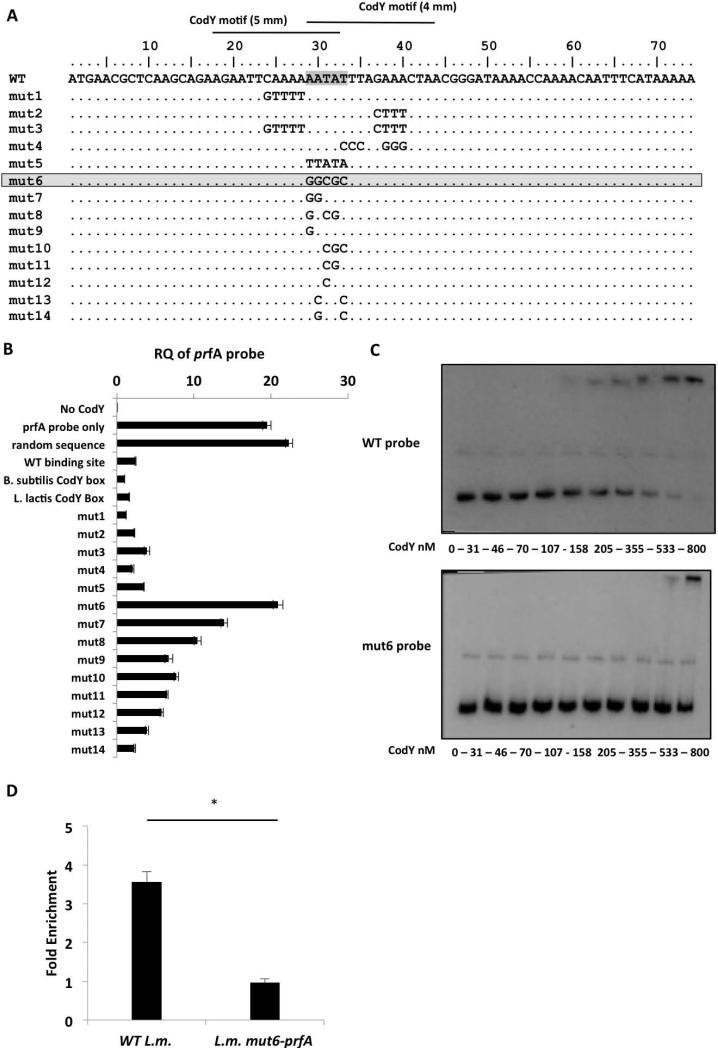
Figure 5. Mutational analysis of the CodY-binding region identifies an AATAT sequence that is critical for CodY binding.
A. Representation of the 74-bp probes synthesized to contain different mutations within the putative CodY-binding region (mut-1 to -14). Critical nucleotides for CodY binding are highlighted. B. A CodY pull-down competition binding assay between the 367-bp prfA probe and each one of the 74-bp competitor probes. The assay is based on a DNA pull down assay using a 6His-tagged CodY protein. Analysis of CodY binding to the prfA probe was done using RT-qPCR with primers specific to the full-length prfA probe. Controls include a sample without CodY (No-CodY), a sample without a competitor (prfA probe only), a sample with random sequence probe as competitor and probes containing the WT prfA CodY-binding site, B. subtilis or L. lactis CodY-boxes as competitors. Results are average of 3 independent biological repeats. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. C. EMSA analysis of CodY binding to prfA 2nd half probe (WT probe) and to prfA 2nd half probe containing the mut6 mutation (mut6 probe). Results are representative of 3 independent biological repeats. D. ChIP-RT-qPCR analysis of CodY binding to WT and L.m. mut6-prfA prfA gene during growth in low-BCAA MM. Results are average of at least 3 independent biological repeats. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD), * represents P value < 0.05.