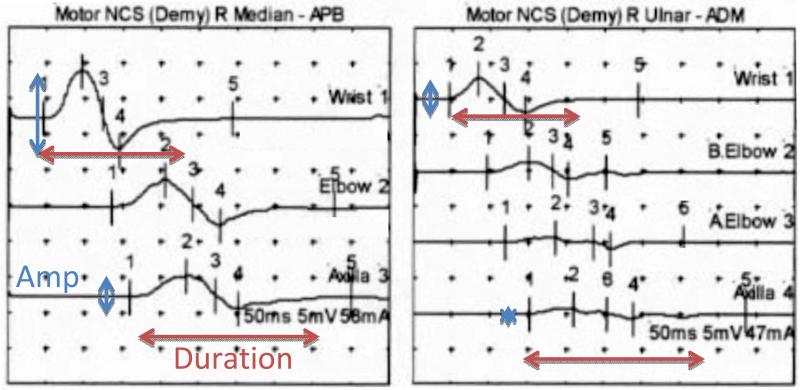
Figure 2.
Median and ulnar motor nerve conduction study showing partial motor conduction block in the forearm segment in a patient with acquired demyelinating polyneuropathy. Note that with stimulation above the elbow, the amplitiude (vertical blue lines) of the motor response is diminished (due to conduction block) when compared with the response at the wrist. Also, the duration of the response (horizontal red lines) is prolonged with stimulation above the elbow due to temporal dispersion, a common feature of demyelination.