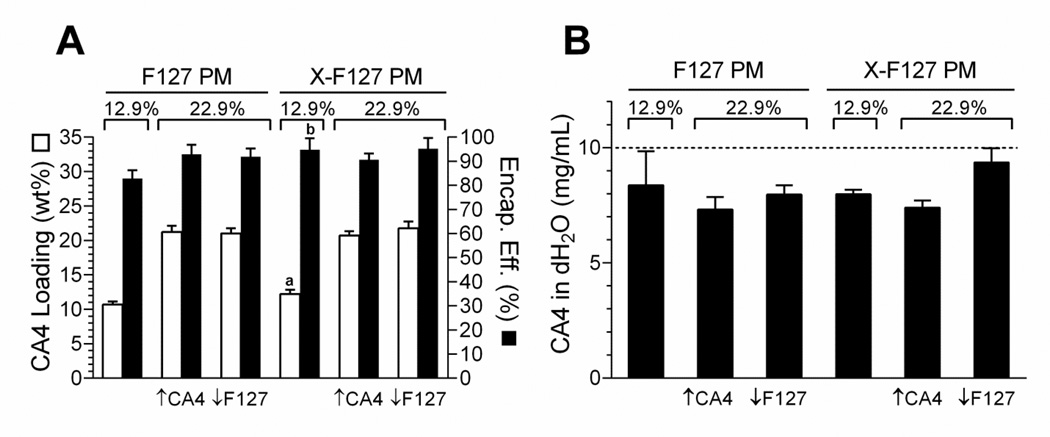
Fig.5.
Effect of peripherally cross-linking the shell of F127 PM on combretastatin A4 (CA4) loading and aqueous solubility. F127 polymer micelles alone (F127 PM) or F127 PM shell cross-linked with ED at 76% of total PEO blocks (X-F127 PM) were loaded with CA4 at 12.9 wt% or 22.9 wt% by the solid dispersion method and lyophilized. Theoretical loading of CA4 was increased from 12.9 wt% to 22.9 wt% by doubling the mass of CA4 (↑CA4) or using half the mass of F127 polymer (↓F127) in the solid dispersion. (A) Average CA4 loading (CA4 wt% of total formulation ± SD, n=3 from the same batch; open bars) and encapsulation efficiency (% of theoretical loading ± SD, n=3; closed bars) of the lyophilized samples were determined by LC-MS/MS and compared by student’s t-test (P <0.05) at 12.9 wt% theoretical loading (P = a0.0255; b0.0251) or by one-way ANOVA with Tukey‧s post-test at 22.9 wt% theoretical loading (P < 0.05). (B) Lyophilized formulations were resuspended in dH2O at a theoretical concentration of 10 mg CA4/mL based on actual CA4 loading determined in (A). Average mg CA4 / mL dH2O ± SD (n=3 independent samples from same batch) in the supernatants was determined by LC-MS/MS and compared to F127 PM at 12.9 wt% CA4 by one way ANOVA with Dunnet’s post-test.