Figure 3.
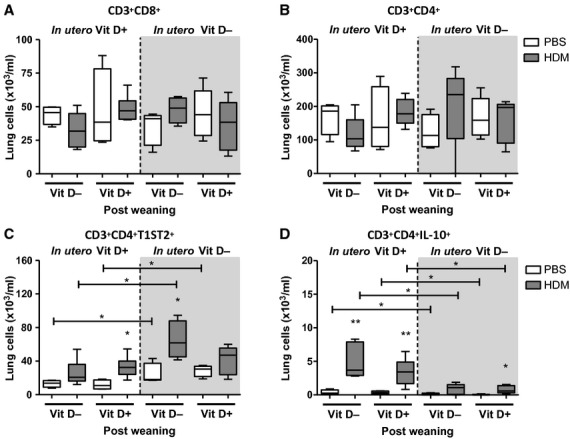
In utero and early-life vitamin D insufficiency skews towards a Th2 environment and reduces T regulatory cells in the lungs of pups. Pregnant female Balb/c mice were fed a vitamin D-deficient diet from day-16 gestation or remained on a normal chow diet. Pups were challenged with house dust mite (HDM) or PBS for 6 weeks. Pups were weaned at 3 weeks of age and either fed a vitamin D-deficient diet or a normal chow. Lung cells were harvested 4 h after last challenge and analysed by flow cytometry. T-cell subsets were defined as CD3+CD8+ (A), CD3+CD4+ (B), CD3+CD4+T1ST2+ (C) and CD3+CD4+IL-10+ (D). + represents vitamin D intake; - represents a lack of vitamin D. Data are expressed as box and whisker plots; horizontal bar represents median, n = 4–6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by Mann–Whitney U-test. Significance refers to HDM and associated PBS control where no line is indicated.
