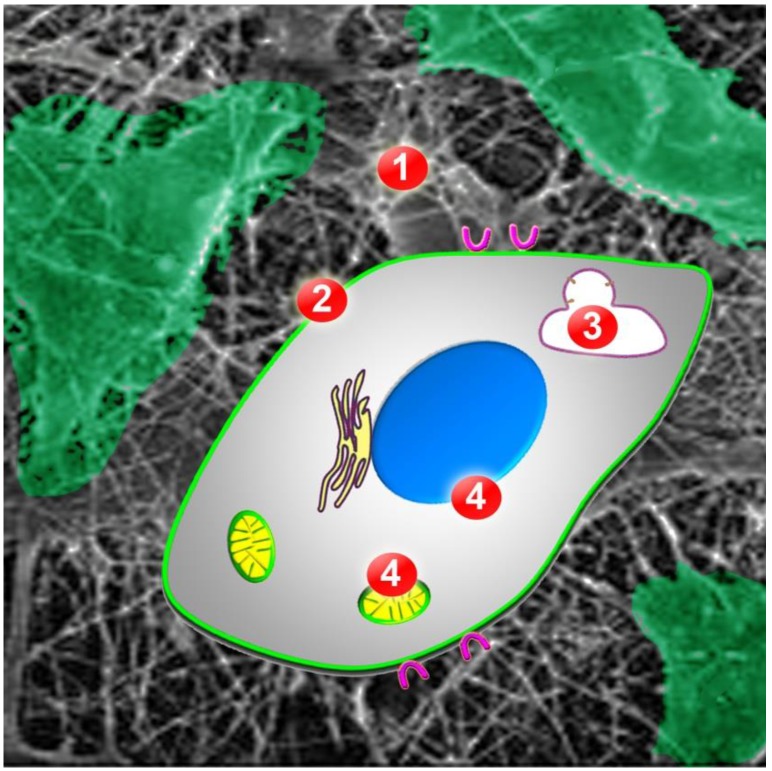
Figure 2.
Obstacles AuNPs have to overcome for successful targeting to intracellular organelles or compartments. Once AuNPs are in the extracellular matrix of the tumor (ECM, barrier 1), they have to bind to the cancer cell surface. Cellular uptake requires translocation across the plasma membrane (barrier 2), by endocytosis or other mechanisms. Inside the cell, AuNPs have to escape from endosomes or lysosomes (barrier 3) to subsequently associate with the desired organelle or cell compartment (barrier 4). Possible final destinations are the nucleus (blue) or mitochondria (yellow).