| Title: | 6,7-Dihydropyrazolo[l,5-a]pyrazin-4(5H)-one Compounds and Their Use as Negative Allosteric Modulators of mGluR2 Receptors | ||
| Patent Application Number: | WO 2014/195311 A1 | Publication date: | 11 December 2014 |
| Priority Application: | EP 13170447.0 | Priority date: | 4 June 2013 |
| EP 13173939.3 | 27 June 2013 | ||
| EP 14166450.8 | 29 April 2014 | ||
| Inventors: | Van Gool, M. L. M.; Alonso-De Diego, S.-A.; Cid-Nunez, J. M.; Delgado-Gonzalez, O.; Decorte, A. M. A.; Macdonald, G. J.; Megens, A. A. H. P.; Trabanco-Suarez, A. A.; Garcia-Molina, A.; Andresgil, J. I. | ||
| Assignee Company: | Janssen Pharmaceutica NV; Tumhoutseweg 30, B-2340 Beerse (BE) | ||
| Disease Area: | CNS disorders | Biological Target: | The metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2 (mGluR2) |
| Summary: | The invention in this patent application relates to 6,7-dihydropyrazolo[l,5-a]pyrazin-4(5H)-one derivatives represented generally by formula (I). These compounds are negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2 (mGluR2) and may be useful for the prevention or treatment of CNS disorders. | ||
| Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are members of group C family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). There are eight known subtypes (named mGluR1–8), which are distributed to various brain regions. They are also compiled into three subgroups based on their pharmacological and structural properties: Group-I (mGluR1 and mGluR5), Group-II (mGluR2 and mGluR3), and Group-III (mGluR4, mGluR6, mGluR7, and mGluR8). mGluRs are activated by binding to glutamate; the activated receptors play an important role in the modulation of synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability in the CNS system. | |||
| While both orthosteric and allosteric modulators of Group-II receptors (mGluR2 and mGluR3) are potentially useful for the treatment of various neurological disorders, antagonists and negative allosteric modulators in particular promise higher potential for the treatment of mood disorders and cognitive or memory dysfunctions. Studies have determined that inhibition of group-II mGluR receptors using either orthosteric antagonists or negative allosteric modulators enhances glutamatergic signaling. This effect is believed to produce antidepressant-like and procognitive effects. Additionally, studies have shown that treatment of mice with group-II mGluR orthosteric antagonists enhances signaling by growth factors such as brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); these growth factors are critically involved in mediating synaptic plasticity. This effect is probably a contributor to both antidepressant and procognitive properties observed by these antagonists. | |||
| Therefore, inhibition of mGluRs of the group-II receptor family, particularly mGlu2, with negative allosteric modulators such as the compounds described in this patent application can potentially provide effective therapy for neurological disorders, including depression and cognitive or memory dysfunctions. | |||
| Important Compound Classes: | 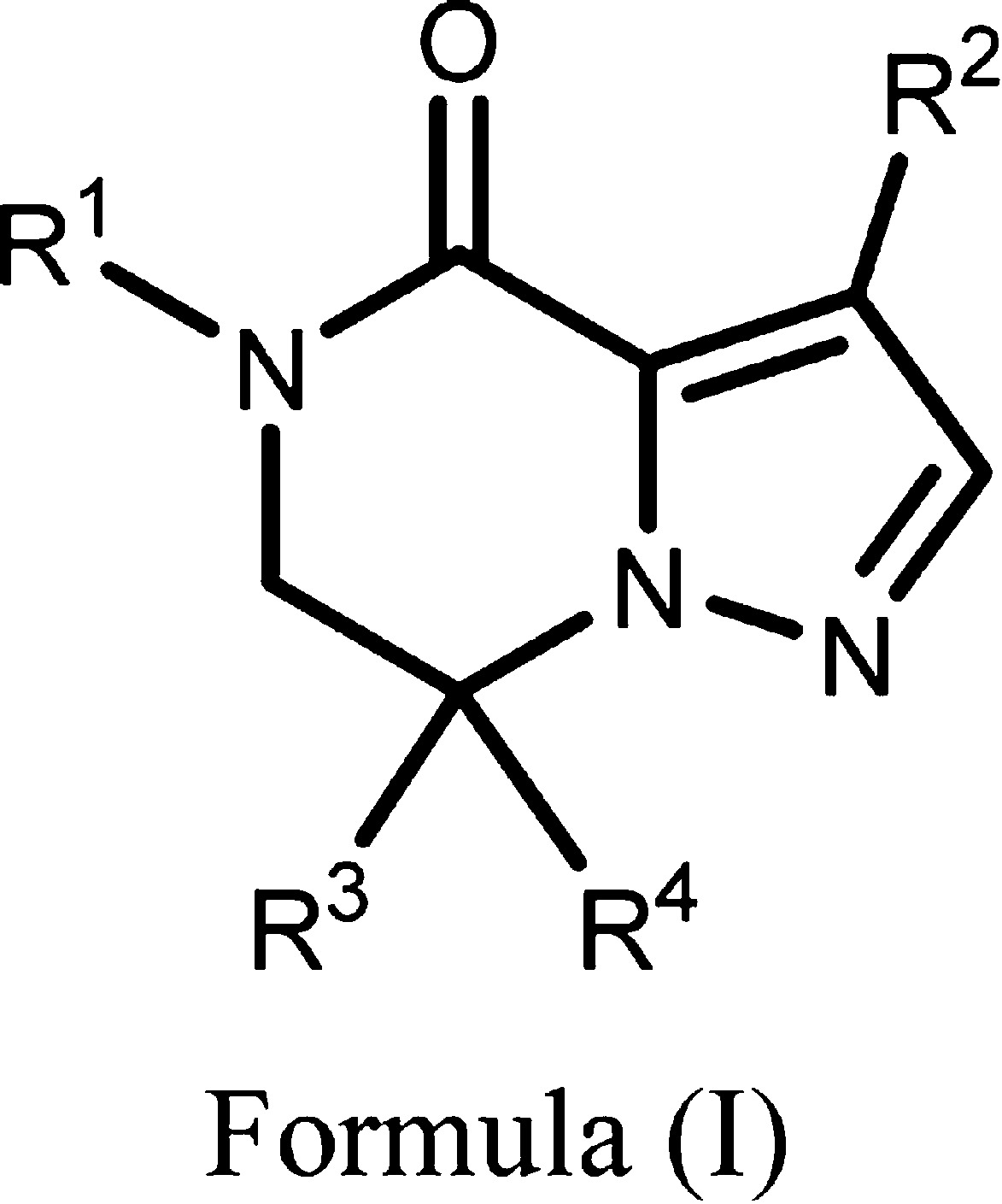 |
||
| Key Structures: | The inventors reported the structures of 267 examples of formula (I) including the following compounds: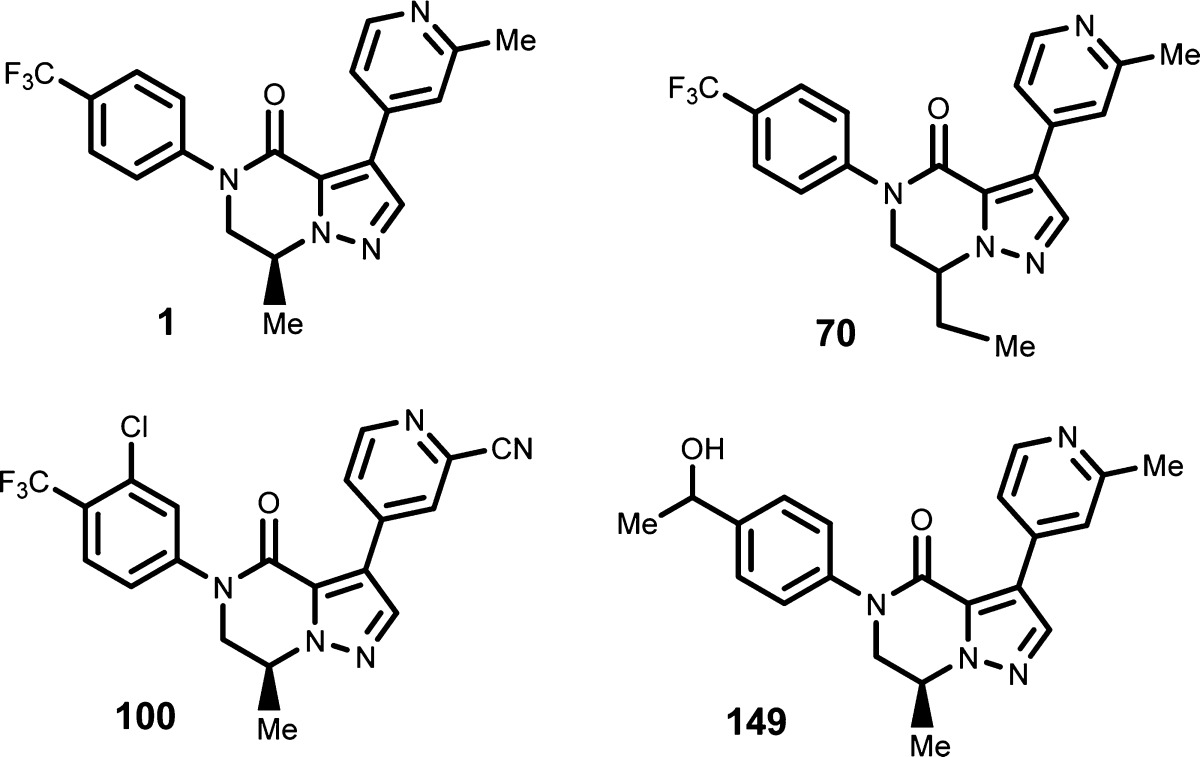
|
||
| Biological Assay: | The following assays were reported for testing the compounds of the invention: | ||
| |||
| Biological Data: | Some results from the [35S]GTPγS binding assay reported for the representative examples of formula (I) are listed in the following table: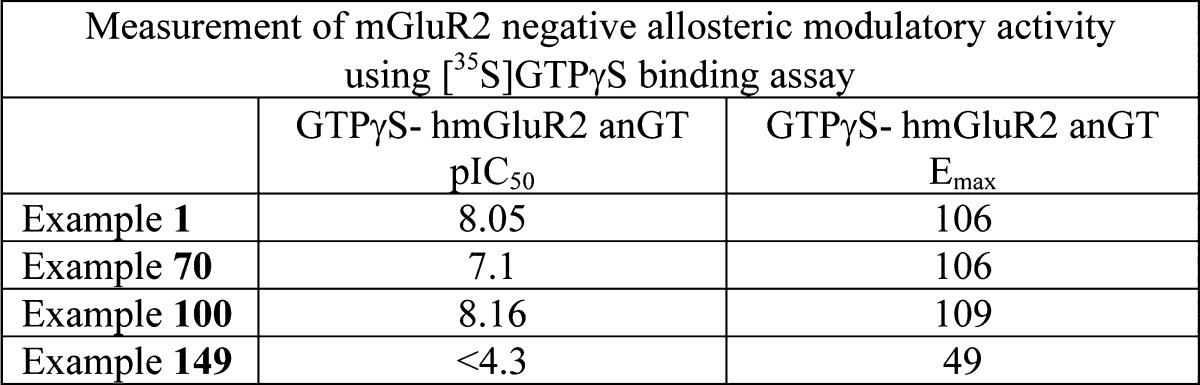
|
||
| Recent Review Articles: | 1. Celanire S.; Duvey G.; Poli S.; Rocher J.-P.. Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 2012, 47, 71–88. | ||
| 2. Rocher J.-P.; Bonnet B.; Bolea C.; Lutjens R.; Le Poul E.; Poli S.; Epping-Jordan M.; Bessis A.-S.; Ludwig B.; Mutel V.. Curr. Top. Med. Chem.; 2011, 11 (6), 680–69. | |||
| 3. Marino M. J.; Conn P. J.. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6 (1), 98–102. | |||

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.