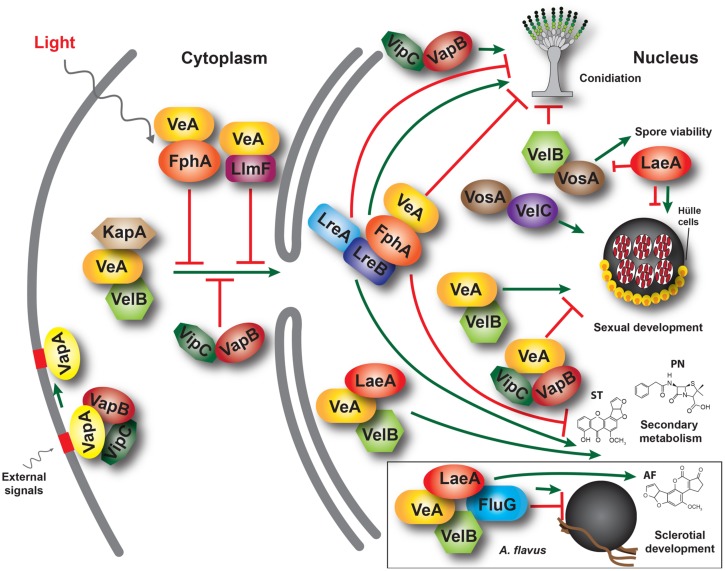
FIGURE 1.
A model illustrating interactions between velvet family proteins, LaeA and other associated proteins in the model fungus Aspergillus nidulans. The α-importin KapA transports the VeA-VelB dimer from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, particularly in the dark. This transport is negatively influenced by other proteins, such as FphA, LlmF and Vip-VapB dimer in the light. In the nucleus, VelB-VeA activates sexual development and can interact with LaeA, forming the velvet complex. VeA also interacts with FphA, which is associated with LreB-LreA forming a light-sensing protein complex. VelB, repressor of asexual development, also forms homodimers and heterodimers with VosA, a protein required for spore viability activating trehalose biosynthesis. VosA also interacts with VelC, which positively regulates sexual development. Additionally, VipC and VapB associate with VeA in the nucleus repressing cleistothecial formation. These complexes regulate development and secondary metabolism in a coordinated manner. VeA, LaeA, and VelB have also been shown to control sclerotial and AF production in A. flavus, where they also form a protein complex, together with FluG (box). ST, sterigmatocystin. PN, penicillin; AF, aflatoxin B1.