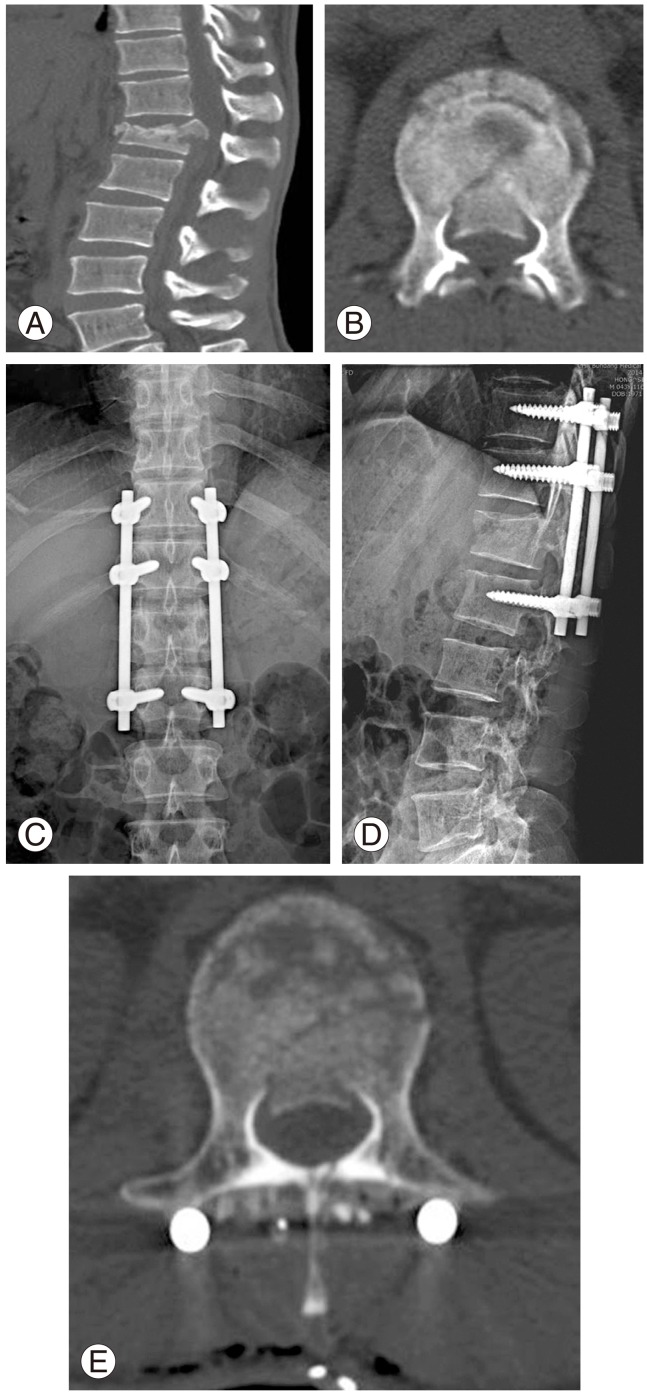
Fig. 1.
A 42-year-old male patient with falling injury. Conus medullaris syndrome was diagnosed with symptoms including loss of perianal sensation, bladder and bowel dysfunction at the time of injury. (A) Burst fractures at L1 on sagittal computed tomography (CT) scan at the time of injury. (B) Around 50% of canal involvement by retropulsed bony fragments on axial CT scan at the time of injury. (C, D) Plain radiographs after indirect reduction and instrumented fusion with posterior approach. (E) Postoperative axial CT scans showing canal decompression by indirect reduction.