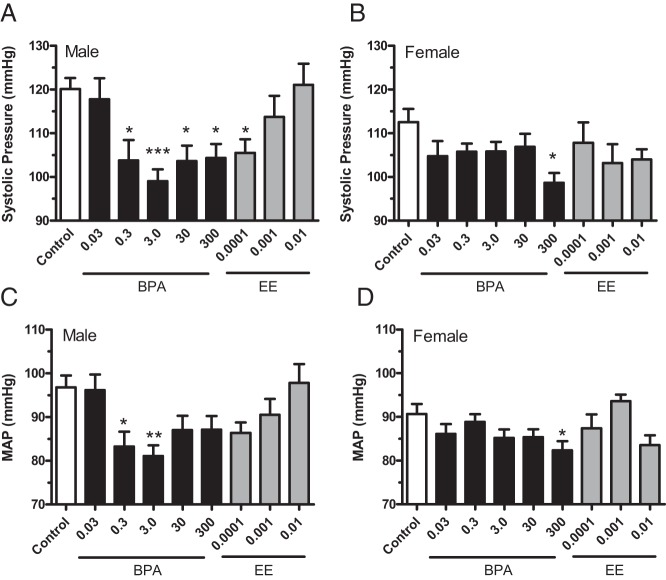
Figure 1.
The BPA- and EE-induced changes in systolic BP and MAP of male and female CD-1 mice exposed to BPA or EE. Blood pressures of 8- to 10-week-old mice were determined by tail-cuff volume pressure recording for male (A and C) and female (B and D) CD-1 mice for each indicated BPA or EE exposure (parts per million). A significant decrease in systolic pressure for 0.3, 3.0, 30, and 300 ppm BPA-exposed groups was detected in males (A) and females (B) exposed to 300 ppm BPA. MAP was significantly reduced in 0.3 and 3.0 ppm BPA treatment groups of males (C) and in 300 ppm BPA in females (B). Data are presented as group mean ± SEM. The level of statistical significance is indicated with asterisks.