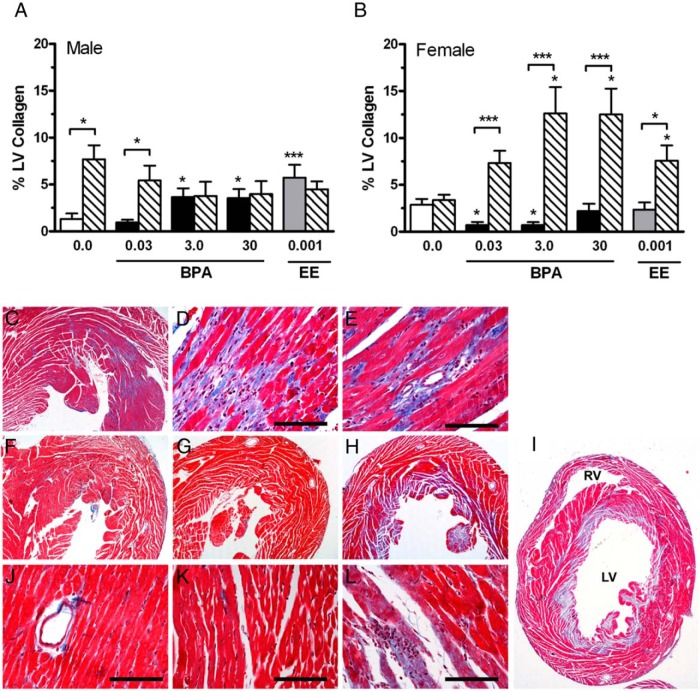
Figure 4.
The impact of BPA and EE on LV collagen and effects of exposures on the hypertropic response to Iso ischemia in male and female CD-1 mice exposed to BPA or EE. A, In 3.0 and 30 BPA and 0.001 EE male exposure groups, a significant increase in LV collagen levels were observed compared with controls. The effects of Iso treatment on collagen accumulation in the LV for each exposure group is indicated by hatched bars. Iso increased collagen in the control and 0.03 ppm exposure groups but had no effect in the 3.0 and 30 BPA and 0.001 EE groups. B, In the female 0.03 and 3.0 BPA exposure groups, a significant decrease in LV collagen was observed compared with controls. Control females were protected from Iso-induced increases in collagen accumulation. Iso significantly increase collagen accumulation in each of the BPA and EE exposures groups. Representative photomicrographs of Masson's trichrome-stained sections of male hearts from the control (C) and 30 ppm BPA exposure groups demonstrate increased interstitial (D) perivascular fibrosis (E). Compared with female controls (F), in the 3.0 BPA exposure group (G), decreased levels of collagen were detected in Masson's trichrome-stained sections of female hearts. In female hearts of the 3.0 BPA exposure group, Iso treatment resulted in a dramatic increase collagen staining (H), which often involved the entire LV endocardium and papillary muscle (I). Areas of infarction-like necrosis with evident myocardial necrosis and numerous infiltrates were common in sections from the 3.0 BPA exposure group (L). RV, right ventricle. Scale bar, 50 μm.