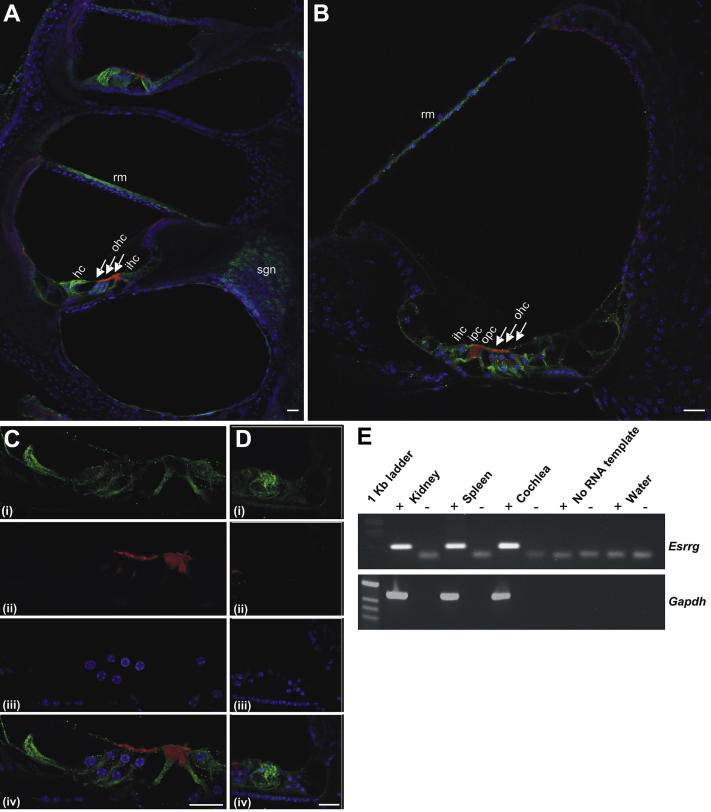
Fig. 2.
Expression of ESRRG in mouse inner ear. (A–D) Results of immunofluoresence with anti-ESRRG in mouse inner ear at P36: anti-ESRRG (green), DAPI (blue), and Phalloidin staining to f-actin (red). (A) Low magnification of mid-apical coil. Strong ESRRG immunoreactivity is localized to Reissner's membrane (rm), Hensen's cells (hc) can be seen in the inner (ihc) and outer (ohc) hair cell region (solid arrows). Weaker immunoreactivity is shown in the spiral ganglion neurons (sgn). (B) Mid magnification of the opposite mid-cochlear coil showing ESRRG immunoreactivity in the organ of Corti localizes to the inner (ipc) and outer (opc) pillar cells and supporting cell bodies and their processes intervening the outer hair cells. (C) High magnification of the organ of Corti. (D) Mid magnification of the opposite apical coil showing strong immunoreactivity in Hensen's cells. Scale bar is 20 μm. (E) Detection of Esrrg mRNAs in P2-P30 rat kidney, spleen, and cochlea tissue using reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction. (RT-PCR). Samples were tested with (+) or without (−) reverse transcriptase (RT) enzyme. No bands were detected in RT (−), in the absence of RNA template or negative control for PCR (water only). Gapdh served as a positive control for mRNA quality.