Figure 6.
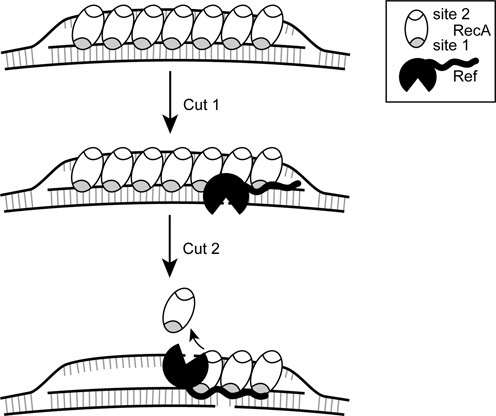
Revised model for the creation of targeted DSBs by Ref. RecA creates a D-loop by binding the targeting oligonucleotide in the primary binding site (gray), and after finding homology, binds the displaced strand in the secondary site (white). The N-terminal domain of Ref binds the paired strand or DNA within the RecA filament groove, positioning the Ref for the first cut. ATP hydrolysis-dependent disassembly of the RecA filament occurs in the 5′→3′ direction. Upon RecA disassembly, Ref can access the displaced strand and create cut 2. The N-terminal domain anchors the Ref protein and a rearrangement occurs to allow the C-terminal nuclease domain access to the displaced strand.
