Figure 5.
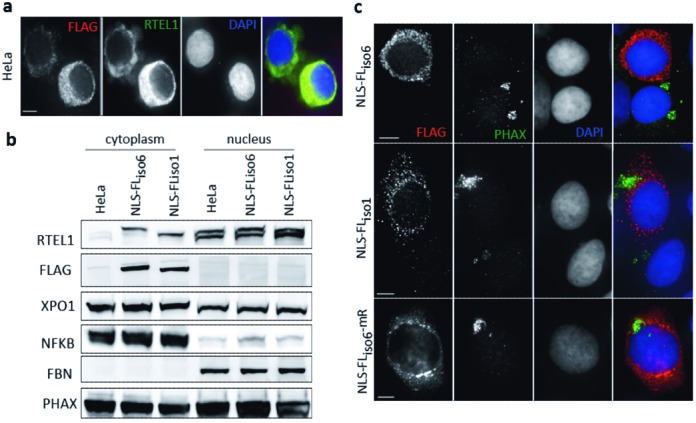
A crucial role of RTEL1 in RNP trafficking occurs in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic versions of RTEL1 were created by mutating the NLS consensus sequence. All NLS-null proteins were flag-tagged allowing its specific detection in IFs (a) and western blots (b). Both approaches confirmed that the NLS null protein remains cytoplasmic. For IFs, cell preparations were fixed in PFA without pre-extraction (scale bar 5 μm). For Western blot (WB), cytoplasmic proteins were extracted with CSK buffer. Nuclear proteins were further extracted in the presence of 600 mM NaCl. Compartmentalization was verified by revealing with antibodies against NFKB (cytoplasmic) and fibrillarin (FBN) (nuclear). (c) An NLS mutated RTEL1iso6 can rescue the cytoplasmic phenotypes induced by a mutated nuclear form of RTEL1. HeLa cells induced for the expression of RTEL1iso6-mR accumulate PHAX in the cytoplasm. Exogenous expression of NLS-null RTEL1iso6 is able to eliminate this phenotype. However, NLS-null RTEL1iso6-mR or RTEL1iso1 (which naturally lacks the RING domain) are not capable of doing this, indicating that the RING domain is crucial for this cytoplasmic activity. Quantitative data can be found in Supplementary Figure S5b. Cell preparations were fixed in PFA without pre-extraction (scale bar 5 μm).
