Figure 3.
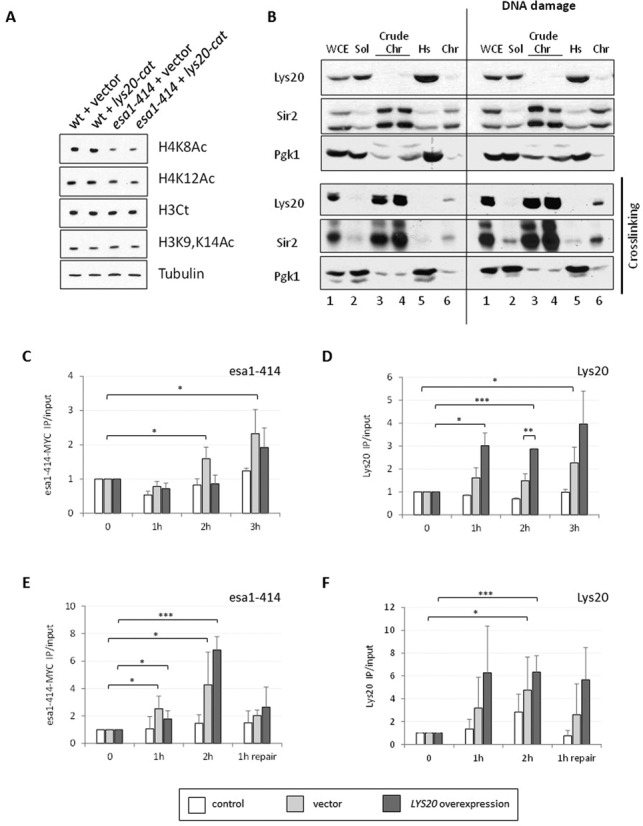
Lys20 was recruited to DNA DSBs with similar kinetics to the HAT Esa1. (A) Increased lys20-cat dosage did not promote increased global histone H4 acetylation. Protein lysates were probed as indicated. Tubulin was included as a loading control. (B) Subcellular fractionation assays revealed that Lys20 binding to chromatin was transient or unstable. The protocol consisted of lysing cells to obtain crude chromatin (Crude Chr) and soluble fractions (Sol). A portion of the crude chromatin fraction was briefly treated with micrococcal nuclease to release polynucleosomes, which were collected with an ultracentrifugation step (Chr). Fractions tested were: whole cell lysate (W), soluble fraction (S), crude chromatin (Crude Chr), high-speed supernatant (Hs) and Chromatin (Chr). The cells were untreated or treated for 90 min with 0.1-M hydroxyurea to induce DNA damage prior to lysate preparation. Anti-Sir2 recognizes two specific bands not observed in a sir2Δ strain, the more rapidly migrating of which is likely to be an N-terminal proteolytic product, since the antiserum was raised to the 13 C-terminal amino acids of Sir2 (not shown). (C) Myc-tagged esa1–414 was recruited 0.2 kb downstream of the DSB at 2 and 3 h after break induction. ChIP anti-Myc of a control untagged strain (white) and of an esa1–414–13MYC tagged strain transformed with vector (light gray) or overexpressing LYS20 (dark gray). The enrichment of Myc-tagged esa1–414 relative to input and to the control locus SCR1 is shown. Time points in all ChIP experiments were time 0 (no HO induction), 1 h of growth in galactose (induction of HO), 2 h in galactose and 3 h in galactose. (D) Lys20 overexpression promoted recruitment 0.2 kb downstream of the break. ChIP anti-Lys20 in the same strains as (C), with control (white) representing a no-antibody control. The enrichment of Lys20 is shown relative to input and to SCR1. (E) Esa1 was enriched 0.6 kb downstream of the DSB 1 and 2 h after break induction. Esa1 no longer bound after repair had started. ChIP anti-Myc in an esa1–414–13MYC tagged strain that can repair by HR because the chromosomal silent mating-type loci are present. The control (white) was an untagged lys20Δ lys21Δ strain, whereas light gray and dark gray columns corresponded to the Myc-tagged strain transformed with vector or with 2μ LYS20, respectively. The enrichment relative to input and to the control locus SMC2 was graphed. Time points tested were as in (C), except with the last time point as 1 h of growth in glucose medium, to repress HO and allow repair by HR. (F) Endogenous Lys20 was recruited to the DSB, however higher levels were recruited when the protein was overexpressed. ChIP anti-Lys20 in the same strains as (E). The control (white) is a lys20Δ lys21Δ strain. The vector strain had endogenous levels of Lys20 expression, whereas the LYS20 sample overexpressed LYS20. Data represent triplicate samples for three independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). The student's t-test was used to assess statistical significance and was represented with asterisks as follows: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.
