Figure 5.
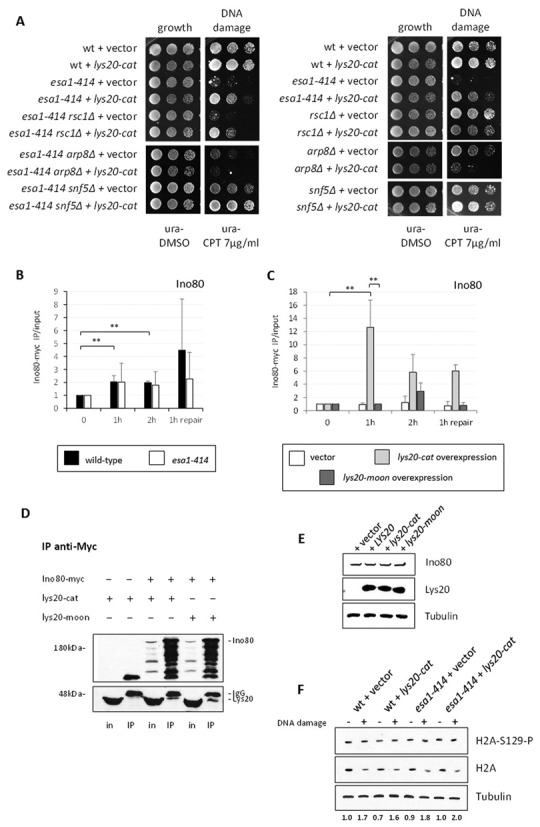
LYS20 overexpression enhanced INO80 recruitment in esa1 cells. (A) Suppression of esa1 by Lys20 overexpression was dependent on the INO80 complex. Double mutants combining esa1–414 with mutants impairing different remodeling complexes were tested for suppression by LYS20 overexpression. Single mutant controls are indicated on the right. Deletion of catalytic subunits of INO80 and RSC is lethal (32,57). The ino80Δ strain is viable in the S288c background, but not in W303, which is used here (27). The INO80 complex (assayed using arp8Δ) proved necessary for suppression by Lys20 as increased dosage of Lys20 antagonized repair when the INO80 complex was disrupted, a result also observed in the single ARP8 null. (B) Ino80 recruitment to the break was similar in wild-type and esa1 cells. ChIP anti-Myc in INO80–9MYC and esa1–414 INO80–9MYC strains. (C) Overexpression of lys20-cat promoted increased recruitment of Ino80, 1 and 2 h after break induction in esa1 cells. ChIP anti-Myc in esa1–414 INO80–9MYC lys20Δ lys21Δ strains transformed with vector, lys20-cat and lys20-moon. Normalization, SD and P-values are the same as in Figure 3. (D) Ino80-myc and Lys20 interacted physically. When Ino80 is precipitated with an anti-Myc antibody, lys20-cat and lys20-moon co-immunoprecipitate. Input (in) and immunoprecipitated (IP) fractions are shown. The first two lanes in each blot were prepared from a strain expressing untagged Ino80 and overexpressing lys20-cat. Lanes 3–6 were from a strain expressing Ino80-myc and lys20-cat or lys20-moon from 2-μ plasmids. Note that compared to whole cell lysates in (E), IP samples of both myc-tagged Ino80 and Lys20 are proteolytically processed. (E) Ino80 protein levels were unaffected by Lys20 overexpression. Whole cell lysates of strains in (C) were probed with anti-Myc. (F) Histone H2A phosphorylation upon DNA damage was normal in esa1 strains transformed with vector or overexpressing LYS20. Protein lysates of the indicated strains were probed with anti-phospho-H2A and anti-H2A antibodies after being treated with hydroxyurea (0.2 M for 90 min). Histone expression is reduced when cells are treated with hydroxyurea (64), thus the damage-induced increase in H2A phosphorylation is only apparent when the H2A phosphorylation signal is quantified relative to H2A levels. Approximately 2-fold induction was observed for all strains tested. The quantification was performed for two independent samples.
