Figure 1.
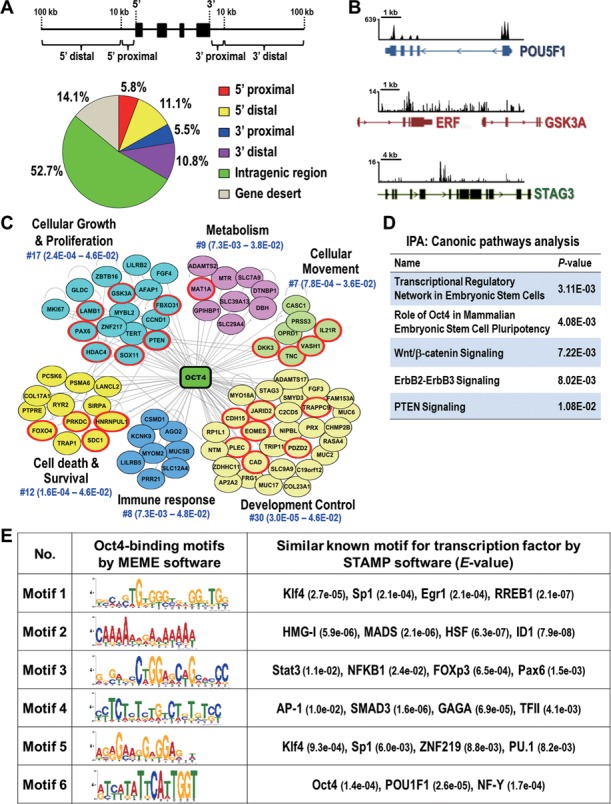
Identification of global binding sites and potential interacting partners of Oct4 in lung cancer cells. (A) Distribution of Oct4 binding sites from ChIP-seq. Schematic diagram illustrates the definition of the location of a binding site in relation to a transcription unit (upper). Pie diagram shows the location of Oct4 binding sites relative to the nearest transcription unit (lower). Gene desert was defined as loci location >100 kb away from the nearest gene. (B) Snapshots of the ChIP-seq binding profiles of Oct4 at POU5F1, GSK3A and STAG3 genes from Integrative Genomics Viewer. (C) Oct4-centered transcriptional network analyzed by Ingenuity-IPA software is shown. Genes validated by qChIP-PCR and qRT-PCR in Figure 2 are in red circle. (D) Top five canonical signaling pathways analyzed by Ingenuity-IPA using gene set from (C). (E) Potential interaction partners of Oct4. Oct4 binding motifs were obtained by MEME software. The potential transcription factor binding sites related to Oct4 targeting motifs were analyzed by STAMP software. The E-value for specific transcription factor is shown.
