Figure 6.
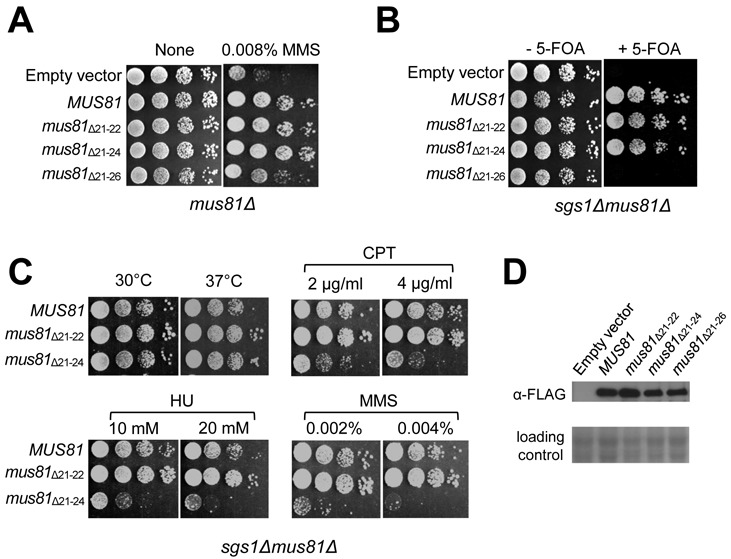
The cellular defects associated with impairment of the N21–26 motif. (A) The MMS sensitivity of mus81Δ21–22, mus81Δ21–24 and mus81Δ21–26 was examined. NJY1777 (sgs1Δmus81Δ + pJM500-URA3-SGS1) strain was transformed with empty vector or vectors containing MUS81, mus81Δ21–22, mus81Δ21–24 and mus81Δ21–26 driven by ADH1 promoter. The transformants were grown until saturation in liquid media and then spotted onto plates without or with different amounts of MMS concentration, which is shown on the top of each panel. The plates were incubated at 30°C for 4 days. (B) The complementation of sgs1Δmus81Δ synthetic lethality by mus81 mutant alleles. The transformants (in panel (A)) were grown until saturation in liquid media and then spotted onto plates with or without 5-FOA. The plates were incubated at 30°C for 4 days. (C) The sensitivity of sgs1Δmus81Δ21–22 and sgs1Δmus81Δ21–24 to CPT, HU and MMS was examined. The colonies that grew on the 5-FOA plates from (B) were inoculated into liquid media until saturation and then spotted onto plates containing indicated amount of DNA damage agents, which are shown on the top of each panel. (D) Analysis of expressions of proteins in 10% SDS-PAGE. The gels were stained with Coomassie blue for loading control (bottom). The expression of Mus81 and its derivatives was confirmed by western blotting using anti-FLAG monoclonal antibodies.
