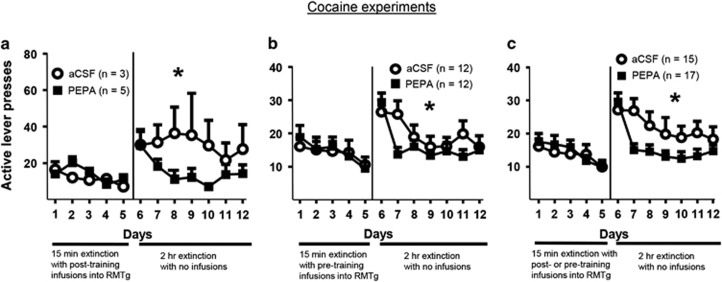
Figure 2.
Effect of RMTg activation on extinction following cocaine self-administration. (a) Active lever presses (mean±SEM) during extinction sessions for those rats receiving post-training intra-RMTg microinjections of PEPA or aCSF. Modified non-cue extinction sessions on days 1–5 were 15 min in length with microinjections given immediately following each session, whereas standard non-cue extinction sessions on days 6–12 were 2 h in length with no microinjections. Those rats that had received PEPA immediately after each session during the modified non-cue extinction sessions showed a more rapid reduction in their active lever pressing on days 6–12. Two-way, repeated-measures ANOVAs of inactive lever pressing found no significant effects of time, group, or interaction for days 1–5 or 6–12 (p>0.05 in all cases; data not shown). (b) Active lever presses (mean±SEM) during extinction sessions for those rats receiving pre-training intra-RMTg microinjections of PEPA or aCSF. Those rats that had received PEPA immediately before each modified non-cue extinction session showed a faster reduction in their active lever pressing on days 6–12 (standard non-cue extinction sessions). Post hoc analysis of the results from days 6 to 12 indicated a significant difference between groups on day 7, the second day of the standard non-cue extinction sessions (p<0.05). Separate two-way repeated-measures ANOVAs of inactive lever pressing found no effect of time, group, or interaction on days 1–5 (p>0.05 in all cases; data not shown) and a significant effect of time (F(6,132)=2.579, p<0.05) and no significant effect of group or interaction on days 6–12 (p>0.05; data not shown). (c) Combined active lever presses (mean±SEM) during extinction sessions for those rats receiving pre- and post-training microinjections. Rats that had previously received PEPA during the modified non-cue extinction sessions (days 1–5), regardless of whether given before or after training, had a more rapid reduction in active lever pressing during the standard non-cue extinction sessions on days 6–12. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVAs were also conducted on inactive lever pressing for days 6–12 of extinction on the combined groups (p>0.05 in all cases; data not shown). *p<0.05, indicating a significant interaction between group and time for days 6–12 in the panel.