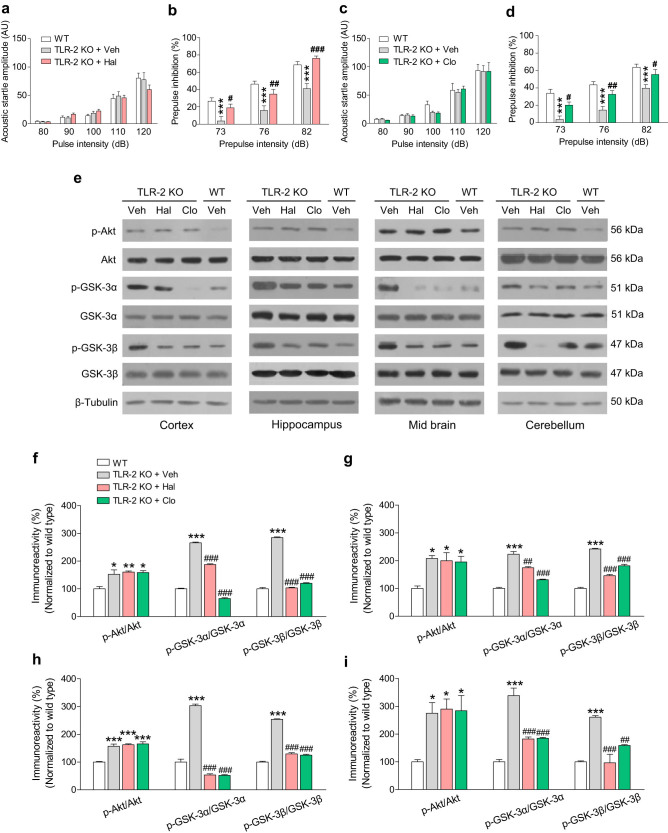
Figure 5. Anti-psychotic drugs attenuated the PPI deficits and activation of Akt-GSK3 signaling in TLR-2 KO mice.
In the acoustic startle response test, acute treatment with haloperidol (Hal, a) or clozapine (Clo, c) did not affect the level of acoustic startle amplitude in TLR-2 KO mice. However, PPI deficits in TLR-2 KO mice were significantly attenuated by the acute administration of haloperidol (b) or clozapine (d), respectively. (e) Immunoblots of p-Akt, p-GSK-3α, and p-GSK-3β were shown in the selected brain regions of TLR-2 KO and WT mouse brains 1 h after the administration of haloperidol or clozapine. The increased expression level of p-GSK-3α and p-GSK-3β, but not p-Akt, was significantly decreased by antipsychotics in the cortex (f), hippocampus (g), midbrain (h), and cerebellum (i) region of TLR-2 KO mice (n = 3 per each group). The gels have been run under the same experimental conditions. All data are shown the mean ± s.e.m. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. WT mice; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. TLR-2 KO mice. Veh, vehicle.