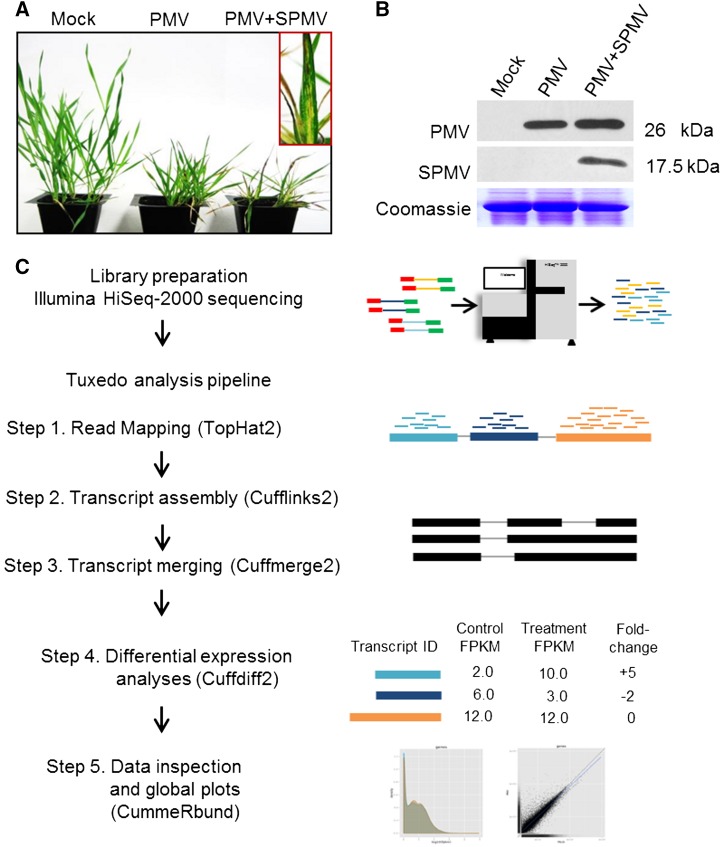
Figure 1.
Typical PMV and PMV+SPMV Disease Symptoms in B. distachyon and Workflow of RNA-seq Analysis.
(A) PMV and PMV+SPMV infection of B. distachyon causes severe chlorosis and necrosis of B. distachyon leaves, stunting, and loss of biomass by 21 dpi (Mandadi and Scholthof, 2012; Mandadi et al., 2014).
(B) Immunoblots of mock, PMV-, and PMV+SPMV-infected plants at 7 dpi showing accumulation of viral capsid proteins in the upper, noninoculated leaves.
(C) Workflow of RNA-seq analysis. RNA isolated from mock, PMV-, and PMV+SPMV-infected B. distachyon shoots at 7 dpi were subjected to 100 base paired-end Illumina HiSeq2000 sequencing, followed by quality trimming and filtering. High-quality reads were retained and mapped to the B. distachyon reference genome (Bd21v1.2) using the TopHat2 program, followed by transcript assembly, differential expression, and global analysis using Cufflinks2, Cuffmerge2, Cuffdiff2, and CummeRbund programs (Tuxedo pipeline) (Trapnell et al., 2010). Normalization of expression data was performed using the FPKM mapped fragments metric (Trapnell et al., 2010).