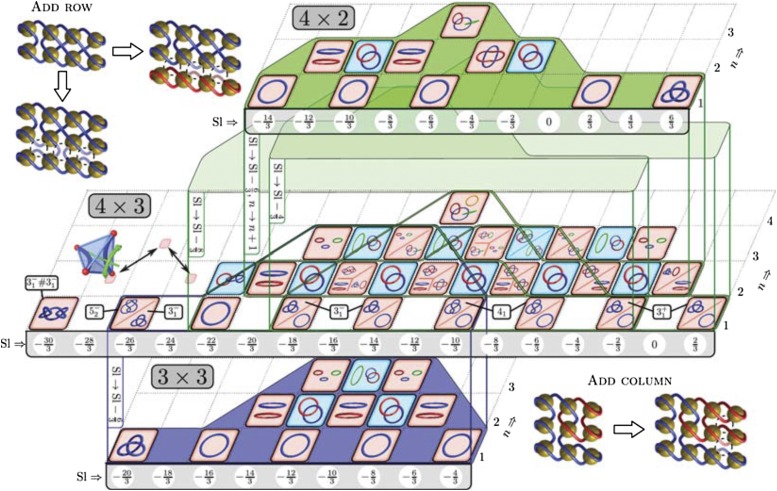
Fig. 5.
A diagram classifies all disclination configurations on a grid, with marked structures that are just extensions of structures on subgrids of dimensions (blue outline) and (green outline). Note that the large grid includes structures, not found on smaller grids. The shifts in the from the smaller grids are marked. Linked and unlinked structures are shaded in blue and red, respectively. (Top Left) Extending a colloidal grid by one row adds an unlinked loop, which can be attached by changing one 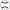 tangle to
tangle to 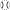 or
or 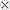 . Resulting structure has the same knot topology as the original one. (Bottom Right) Attached column preserves the knot if all of the added tangles are of
. Resulting structure has the same knot topology as the original one. (Bottom Right) Attached column preserves the knot if all of the added tangles are of 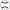 type. Linking and orientation preserving rewirings of a single tangle switches between diagonally adjacent structures that form a triangle, as shown on the left side of the main diagram. Chiral single-component knots are marked with a “±” sign according to the sign of the exponent of the highest-order term in the Jones polynomial.
type. Linking and orientation preserving rewirings of a single tangle switches between diagonally adjacent structures that form a triangle, as shown on the left side of the main diagram. Chiral single-component knots are marked with a “±” sign according to the sign of the exponent of the highest-order term in the Jones polynomial.