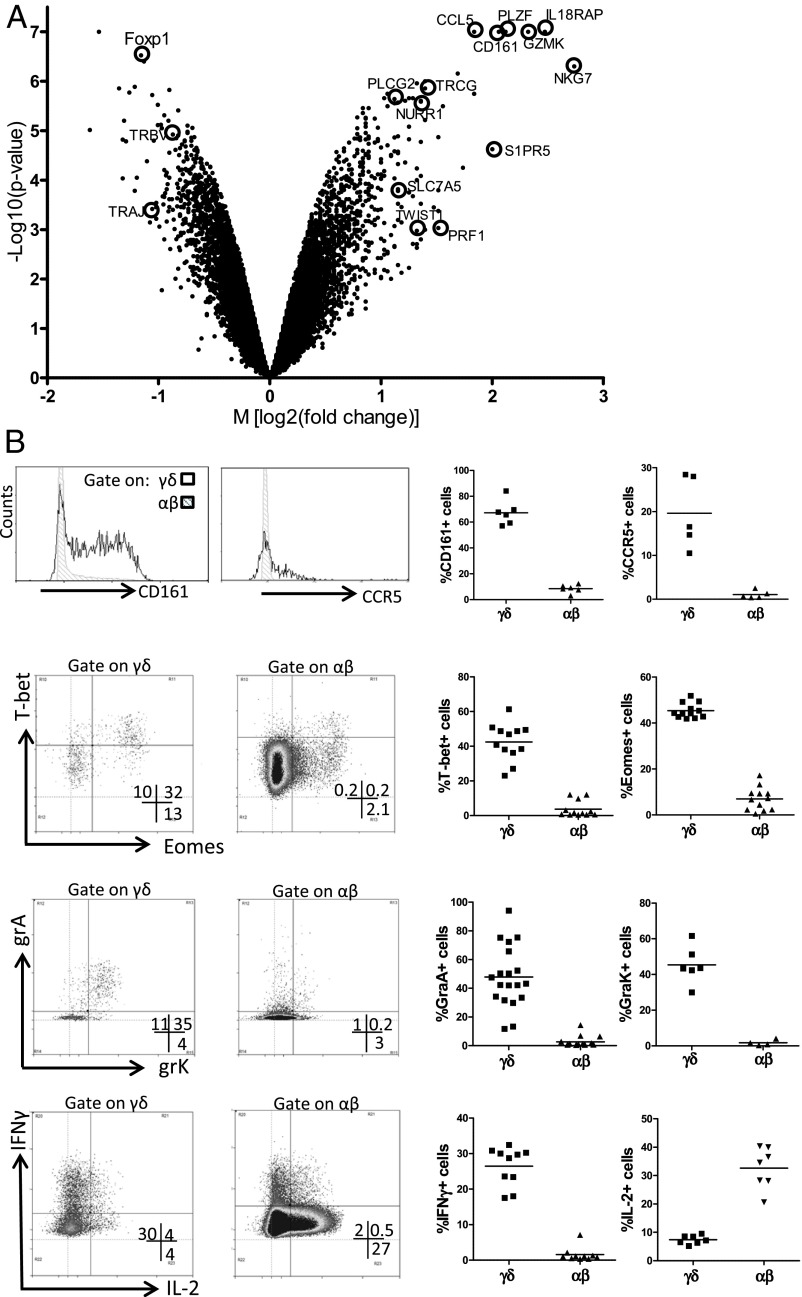
Fig. 5.
Fetal blood Vγ9Vδ2 T cells are preprogrammed effectors. (A) Volcano plot of genes that are differentially expressed in Vγ9Vδ2 γδ T cells and αβ T cells sorted from fetal blood (n = 4; <30 wk gestation). Each dot indicates one gene according to its M value [log2 (fold change)] and P value [log10 (P value)]. Several of the genes highly enriched within Vγ9Vδ2 γδ T cells (positive M values) and αβ T cells (negative M values) are indicated. (B) Fetal blood γδ and αβ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for CD161 (n = 6), the chemokine receptor CCR5 (n = 5), the transcription factors T-bet (n = 12) and eomes (n = 12), the granzymes A (n = 19) and K (n = 6), and, after 4-h stimulation with PMA/ionomycin, for the cytokines IFN-γ (n = 10) and IL-2 (n = 7). (Right) Each dot in represents the data for one fetus after gating on either γδ (CD3+γδ+ lymphocytes) or αβ (CD3+γδ− lymphocytes) T cells. (Left) Representative flow cytometry plots, after gating on either γδ or αβ T cells. Note that, because of the very high percentage of the Vγ9Vδ2 subset within γδ T cells before 30 wk gestation, results were similar when gating on total γδ+ cells or on the Vγ9+Vδ2+ subset that was specifically gated in some experiments. CCL5, RANTES; CD161, NKR-P1A, KLRB1; Foxp1, Forkhead box protein P1; GZMK, granzyme K; IL-18RAP, IL-18 receptor accessory protein; NKG7, natural killer cell group 7; NURR1, nuclear receptor-related 1; PLCG2, phospholipase C, gamma 2; PRF1, perforin; S1PR5, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 5; SLC7A5, a system L amino acid transporter; TWIST1, Twist-related protein 1; PLZF, promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger, ZBTB16; TRAJ, T-cell receptor α joining; TRBV, T-cell receptor β variable; TRGC, T-cell receptor γ constant.