Figure 3.
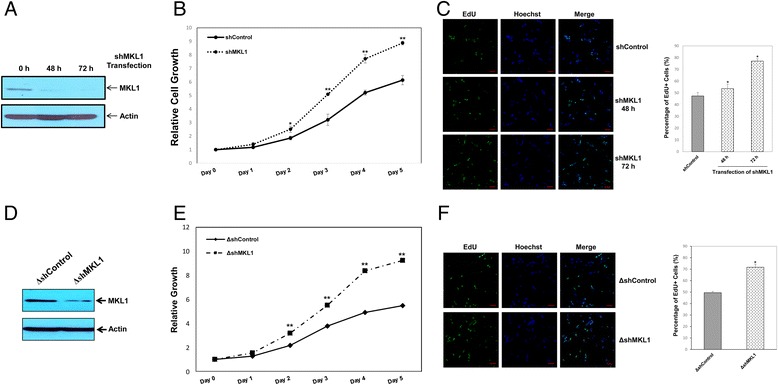
Knockdown of MKL1 promotes cell cycle progression through S phase. A) MPC5 cells were transiently transfected with a MKL1-specific shRNA plasmid (shMKL1) or a scrambled shRNA control plasmid (shControl) and cultured at 33°C. The efficiency of MKL1 protein knockdown was examined by western blotting. Actin was used to normalize MKL1 levels. B) At the indicated time points, cell growth was measured using the CCK-8 assay. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the control (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test). C) Cell proliferation was measured by immunofluorescence analysis of EdU incorporation. Scale bars, 25 μm. The percentage of proliferating cells was calculated as EdU-positive cells/Hoechst-stained cells × 100%. *p < 0.05 compared with the control (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test). D) MPC5 cells were stably transfected with a MKL1-specific shRNA plasmid (ΔshMKL1) or a scrambled shRNA control plasmid (ΔshControl) and cultured at 33°C. Expression of MKL1 protein was verified by western blotting. Actin was used to normalize MKL1 levels. E) At the indicated time points, cell growth was measured using the CCK-8 assay. **p < 0.01 compared with the control (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test). F) Cell proliferation was measured by immunofluorescence analysis of EdU incorporation. Scale bars, 25 μm. The percentage of proliferating cells was calculated as EdU-positive cells/Hoechst-stained cells × 100%. *p < 0.05 compared with the control (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test).
