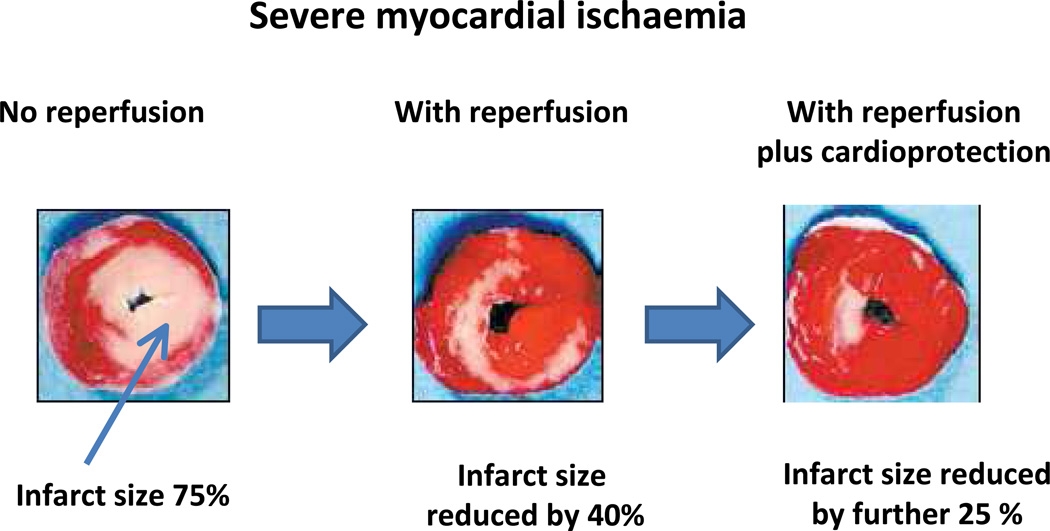
Figure 3. Reduction of infarct size.
In acute myocardial ischaemia rapid reperfusion decreases infarct size variably, roughly by about 40%, leaving 30% still damaged by lethal reperfusion injury. With molecular cardioprotection or pharmacologic agents that inhibit reperfusion injury, the final myocardial infarct size may be rescued by a further 25% thereby achieving a much smaller final infarct. Remote Ischaemic conditioning is a simple non-invasive method of reducing final infarct size.