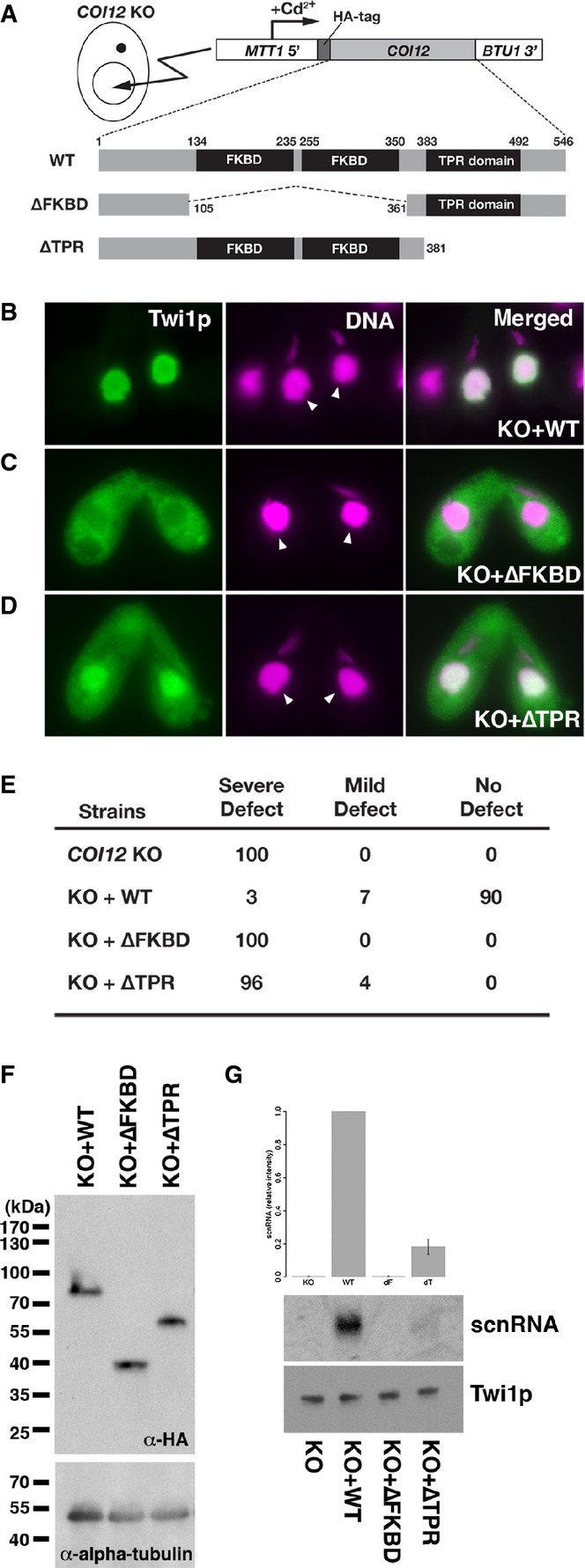
Cells containing the expression constructs shown in (A) were mated with
COI12KO cells in the presence of cadmium ions. The localization of Twi1p was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining using an anti-Twi1p antibody at 3 hpm (B–D). In (B–D), the parental MACs are marked with arrowheads. DNA elimination was analyzed by DNA FISH with probes against Tlr1 IESs at 36 hpm (E). Defects in DNA elimination were categorized as described for Fig
1C. The expression of the different Coi12p mutants was analyzed by Western blot using an anti-HA antibody (F, top). Alpha-tubulin was analyzed as a loading control (F, bottom). The Twi1p-containing complex was immunoprecipitated with an anti-Twi1p antibody. Precipitated scnRNA was separated on a denaturing gel and visualized by the nucleic acid staining dye GelRed (G, top and middle). The intensities of bands relative to the sample with the mating expressing wild-type Coi12p (KO+WT) are shown on the top, and a result of a representative experiment is shown in the middle. Precipitated Twi1p was analyzed by Western blot using an anti-Twi1p antibody (bottom). In (G), the standard deviation (SD) between technical replicates is indicated.