Fig. 7.
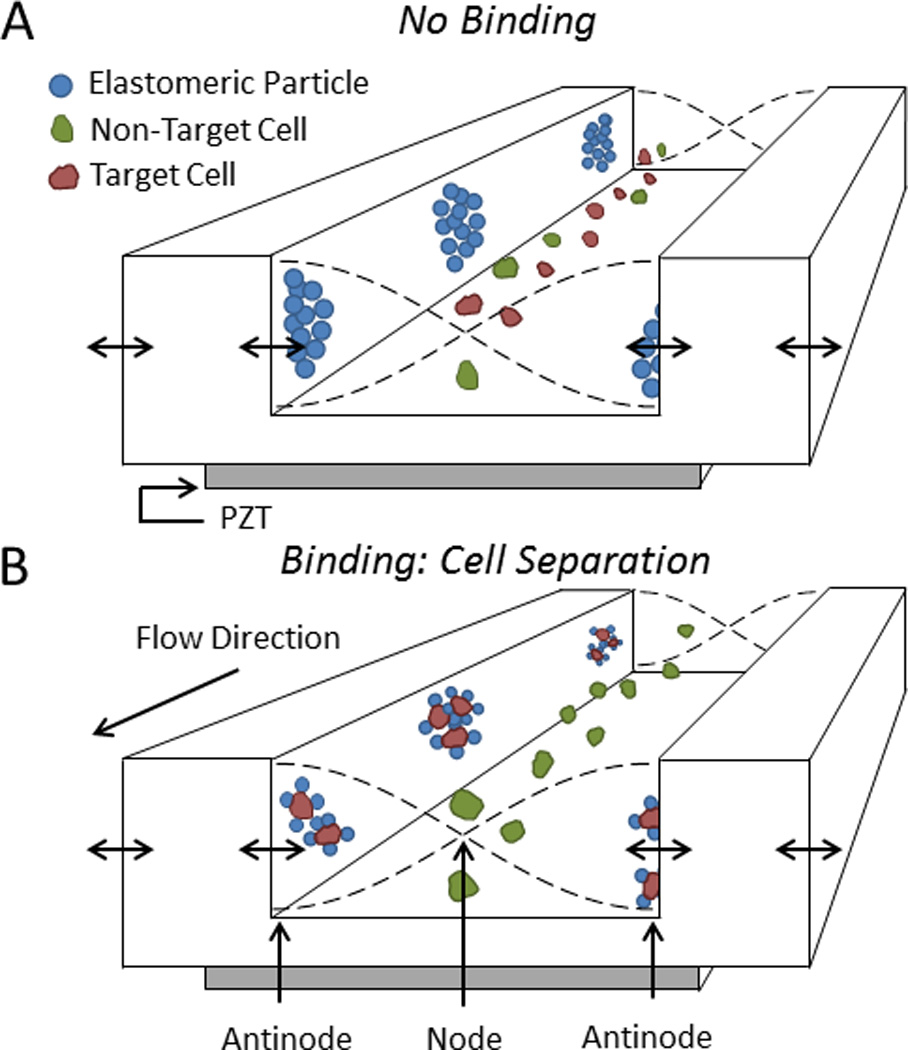
Acoustic separation of cells using elastomeric particles. A) Elastomeric particles and cells focus to the antinodes and node(s) of an acoustic standing wave, respectively. B) When elastomeric particles bind to target cells, those complexes displace to the pressure antinodes for separation from non-target cells. Adapted from Shields IV et al50 2014 American Chemical Society.
