Figure 3.
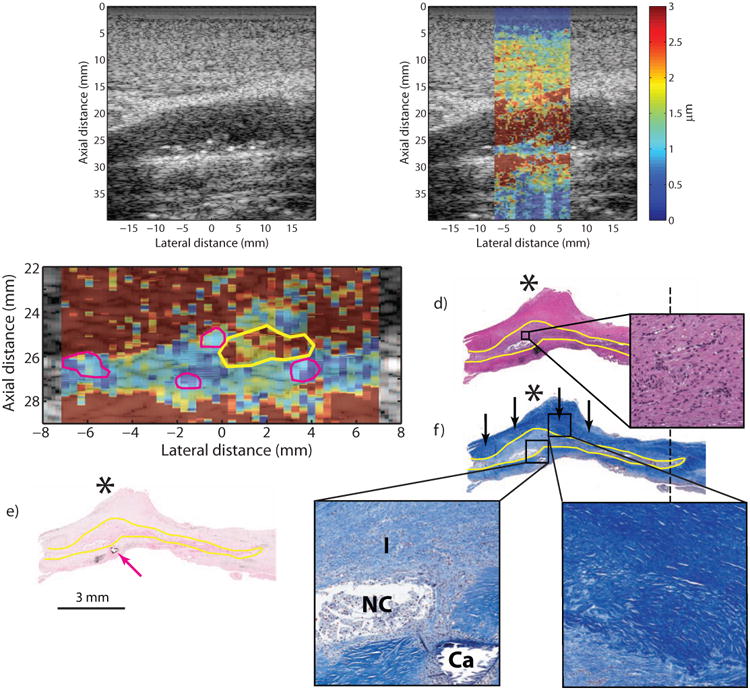
Type Va plaque from the ICA of a 53 year-old, symptomatic female (patient B). B-mode image (a) shows a plaque on the distal wall with a protruding shoulder region (a, asterisk) and a number of small echogenic foci scattered throughout (white arrows). ARFI imaging (b) shows that the area beneath the shoulder region displaces farther than the rest of the plaque. ARFI magnification image is shown in (c); the solid white outline indicates extent of the plaque in the ultrasound image, the yellow outline indicates the higher displacing region, and magenta outlines indicate echogenic foci. Histological staining with H&E (d) and VK for calcium (e) shows a type Va plaque with a protruding shoulder region (d, asterisk) and small, submillimeter calcifications (e, magenta arrow). LMT staining for collagen shows abundant fibrosis in the shoulder region, indicated by the deep blue color (f, black arrows), which covers a cellular area with inflammation and a small, developing necrotic core. Inset panels show higher-magnification images of the cellular area just above the necrotic core (d.1), the cellular area with the necrotic core (f.1) and the fibrous cap (f.2). The region of inflammation from histology is outlined in yellow. ICA, internal carotid artery; CCA, common carotid artery; LMT, Lillie's modified Masson's trichrome; VK, Von Kossa; I, inflammation; NC, necrotic core; CA, calcium.
