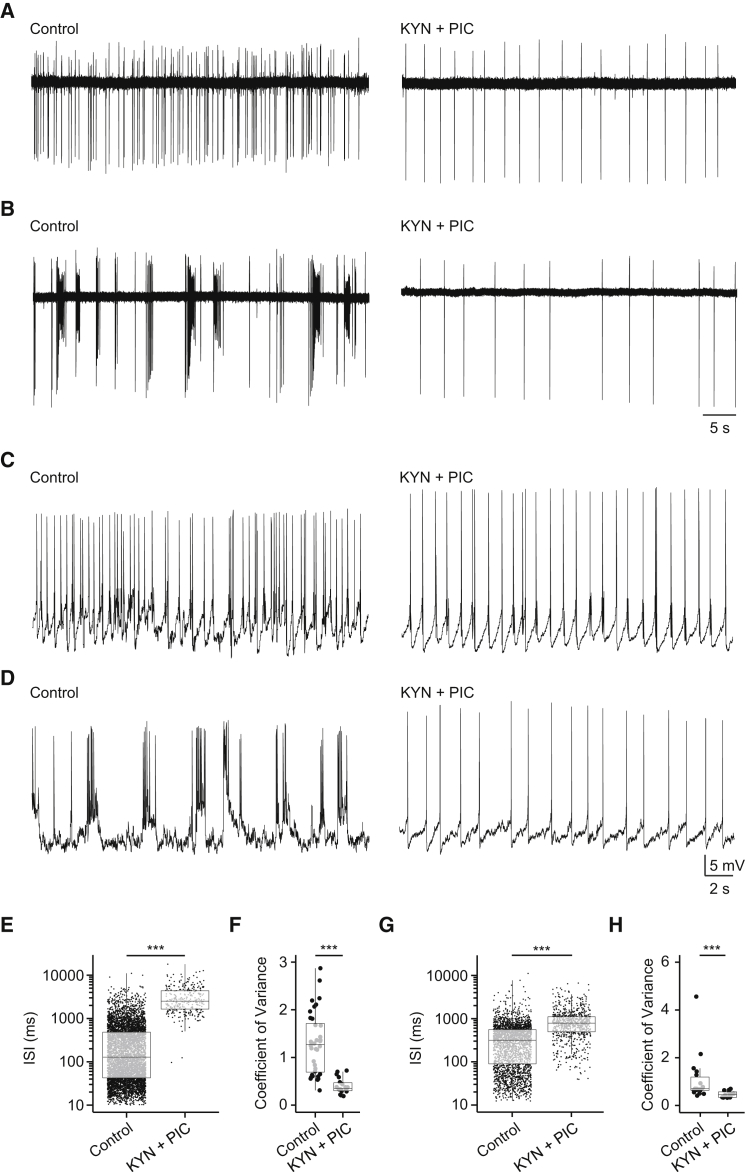
Figure 4.
Autonomous Spike Activity in DDNs
(A–D) Left: extracellular loose (A and B) and perforated (C and D) patch clamp recordings of DDN activity in awake, paralyzed larvae bathed in control saline. Traces in (A)–(D) are derived from different DDNs. Right: effects of kynurenic acid (2–4 mM) and picrotoxin (50–100 μM) on DDNs that exhibit tonic and intermittent burst spiking (A and C) or repetitive burst spiking (B and D). Note that addition of these blockers unmasks low-frequency autonomous spiking activity.
(E–H) Box-and-whisker plots showing the effects of synaptic blockers on interspike interval (ISI; log scaled) and coefficient of variation in loose (E and F) and perforated (G and H) patch clamp recordings. In (E)–(H), filled circles depict raw data points; upper and lower hinges of the box correspond to the first and third quartiles; whiskers extend to 1.5× the interquartile range; and lines within boxes represent median.
Scale bars of (A) and (B) are shown in (B); scale bars of (C) and (D) are shown in (D). See also Figure S2.