Figure 3.
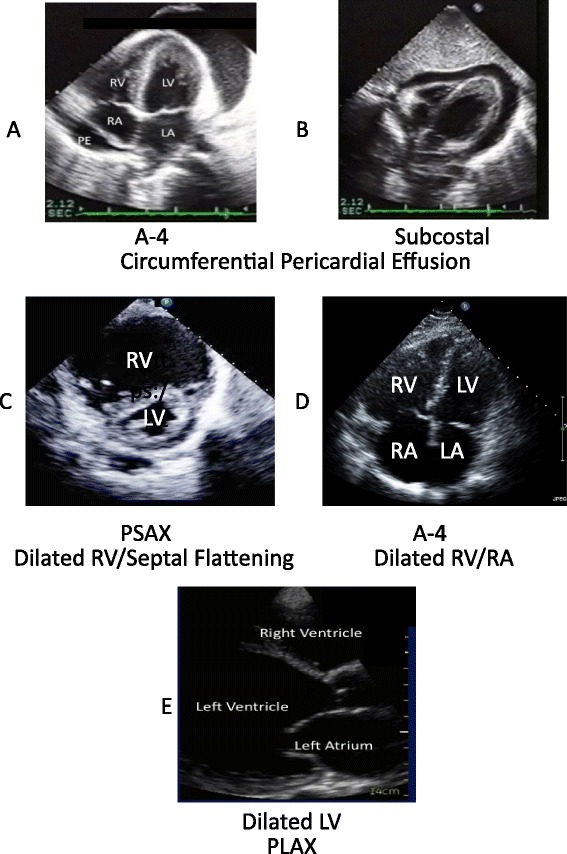
Examples of pathological findings. (A) Apical four chamber (A-4) view. Circumferential pericardial effusion. Left ventricle (LV), right ventricle (RV), left atrium (LA), right atrium (RA), and pericardium with a circumferential echocardiographic-free space or pericardial effusion (PE). (B) Subcostal view. LV, RV, LA, RA, and pericardium with a circumferential pericardial effusion. Diastolic right ventricular ‘buckling’ or collapse is demonstrated. (C) Parasternal short-axis view (PSAX) of the RV and the LV. The RV is dilated. The interventricular septum demonstrates ‘flattening’ or ‘displacement’, indicating evidence of RV pressure or volume overload. (D) A-4 view. Dilated RV, dilated RA, LV, and LA. (E) Parasternal long axis (PLAX) view of the RV, dilated LV, aorta, and LA.
