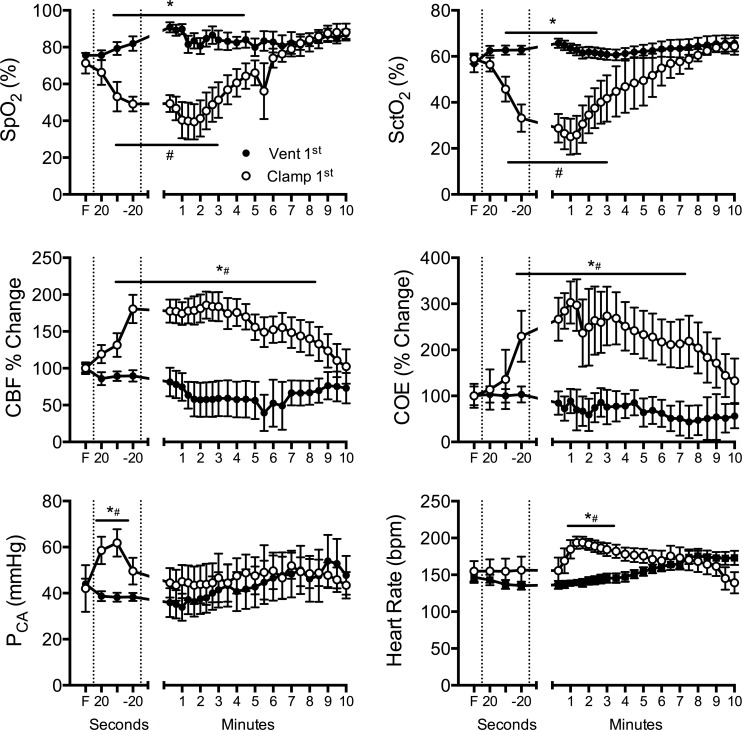
Fig 3. Arterial and cerebral oxygen saturation and haemodynamics.
(A) Arterial saturation of oxygen measured by pulse oximetry (SpO2), (B) cerebral oxygenation (SctO2), (C) cerebral blood flow (CBF), (D) cerebral oxygen extraction (COE), (E) arterial pressure measured in a carotid artery (PCA) and (F) heart rate measured in Vent 1st (closed circles) and Clamp 1st (open circles) preterm lambs. First dashed line indicates ventilation onset for Vent 1st lambs or umbilical cord clamping for Clamp 1st lambs; second dashed line indicates umbilical cord clamping for Vent 1st lambs and ventilation onset for Clamp 1st lambs. F = fetal value. * indicates significant difference Vent 1st vs. Clamp 1st (p<0.05). # indicates time difference from fetal (F) value (p<0.05). In the time between umbilical cord clamping and ventilation onset, Clamp 1st lambs significantly reduced arterial and cerebral oxygen saturation, and increased CBF and oxygen extraction to compensate. Ventilation onset increased arterial and cerebral oxygen saturation back to Vent 1st lambs values by 5 min. Vent 1st lambs maintained steady oxygenation and haemodynamics during the same time.