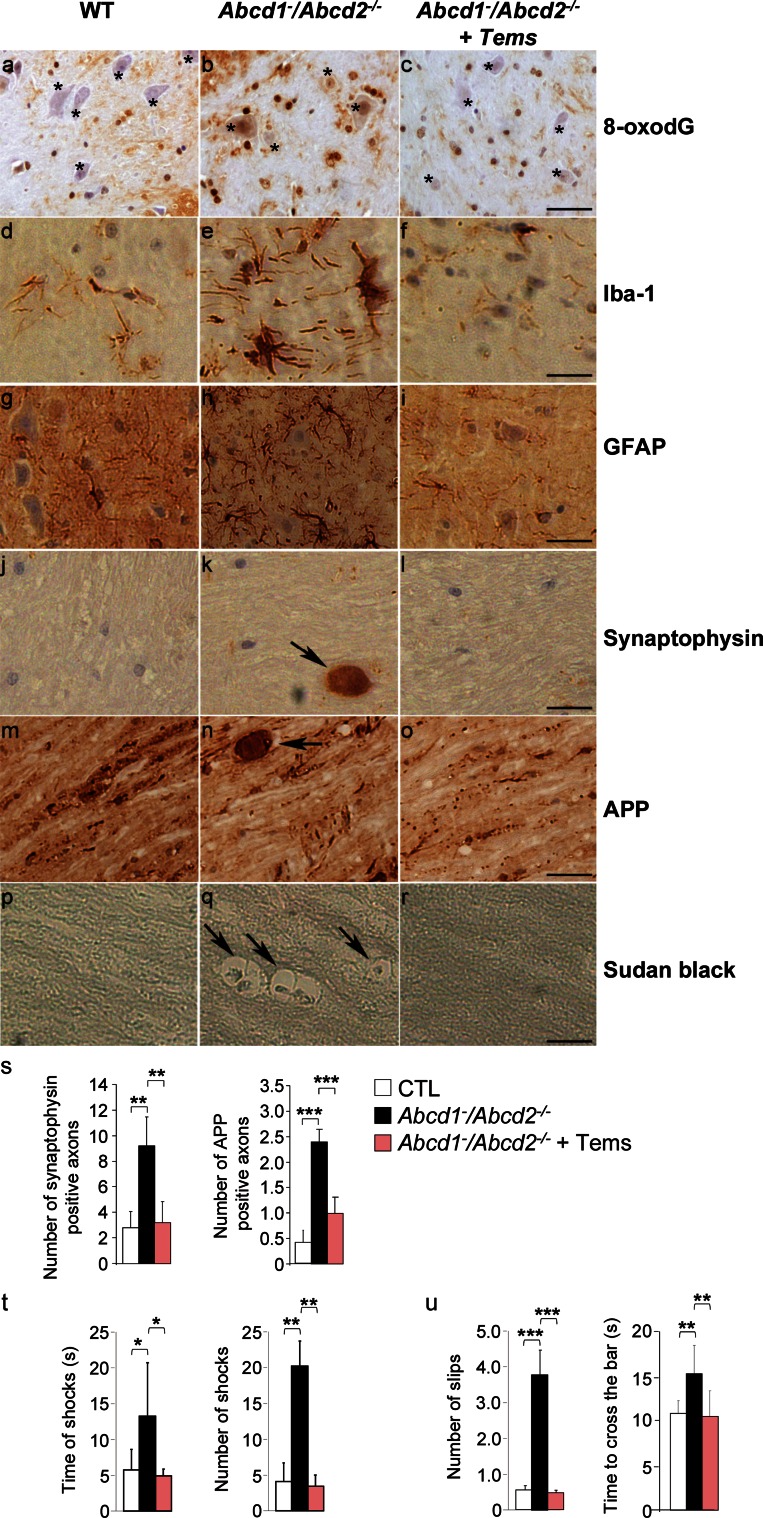
Fig. 6.
Temsirolimus prevents oxidative stress and myelin and axonal pathologies in spinal cords of 17-month-old Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− mice. Temsirolimus rescues locomotor deficits in Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− mice. a–s Immunohistological analysis of axonal pathologies performed in 17-month-old WT, Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− and Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− mice treated with temsirolimus (Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− + Tems). Spinal cord immunohistological sections were processed for a–c 8-oxodG, d–f Iba-1, g–i GFAP, j–l synaptophysin, m–o APP and p–r Sudan black. Representative images a, d, g, j, m and p for WT, b, e, h, k, n, and q for Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/−, and c, f, i, l, o and r for Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− + Tems mice are shown. Bars 25 µm. Small star indicates the motor neurons in a, b and c. s Quantification of synaptophysin and APP accumulation in spinal cord immunohistological sections of WT, Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− and Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− + Tems mice. t Treadmill test and u bar cross test have been carried out in 17-month-old WT Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− and Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− mice treated with temsirolimus (Abcd1 − /Abcd2 −/− + Tems). t The latency to falling off the belt (time of shocks) and the number of shocks received were computed after 5 min. u The time spent to cross the bar and the numbers of slips were quantified. Values are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5 per condition in a–s; n = 12 in t and u; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s hsd post hoc test)