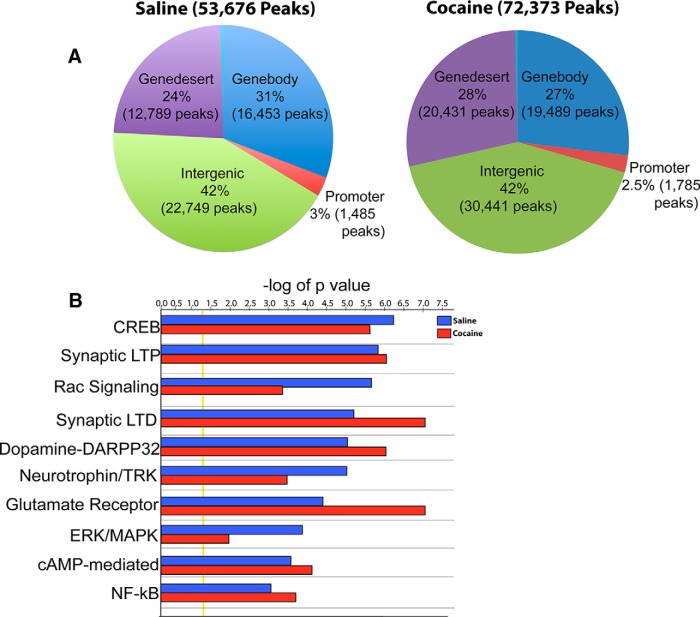
Figure 1.
ChIP-seq reveals genomic target regions for SIRT1 binding in NAc under saline and cocaine conditions. ChIP-seq reveals relatively even distribution of SIRT1 binding across genomic regions in NAc. A, Genome-wide occupancy of SIRT1 in saline (53,676 peaks) and chronic cocaine (72,373 peaks) (20 mg/kg) conditions. Regional analysis of genomic regions in NAc from both saline- and cocaine-treated mice reveals that ∼70% and 30% of SIRT1 peaks reside in intergenic/gene desert and promoter/gene body regions of the genome, respectively. B, SIRT1 regulates canonical signaling pathways implicated in synaptic and behavioral plasticity. The analyses shown were performed on averages of 3 saline and 3 cocaine replicates. Pearson's correlation analysis revealed strong consistency (>75%) between each replicate in the saline and cocaine groups.