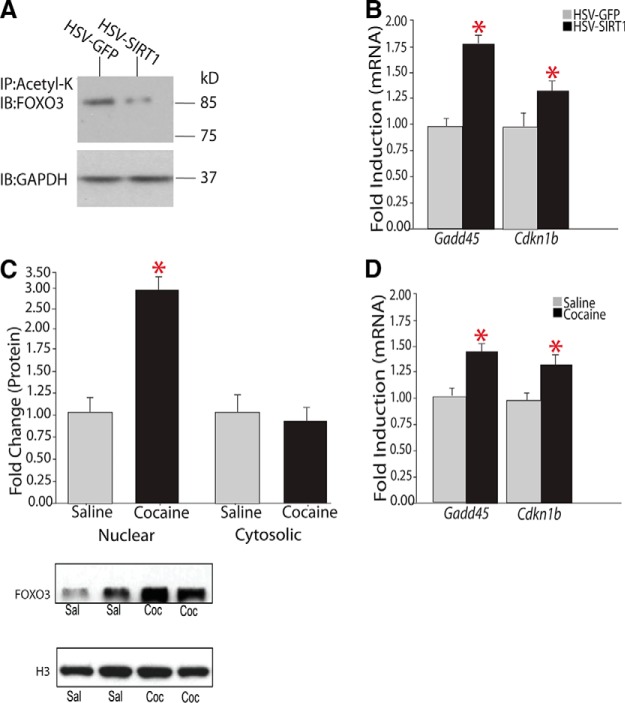
Figure 6.
Regulation of the FOXO3a signaling pathway in NAc by SIRT1 and cocaine. A, Representative Western blot of immunoprecipitated pan-acetyl-K from NAc of mice injected with HSV-GFP or HSV-SIRT1 and probed with an anti-FOXO3a or -GAPDH antibody. HSV-SIRT1 deacetylates FOXO3a. Each lane represents pooled tissue from bilateral NAc punches from 5 mice. Results are representative of 5 replications. B, HSV-SIRT1 in NAc increases the induction of two known FOXO3a target genes, Gadd45α (HSV-GFP, 1.00 ± 0.10, n = 10; vs HSV-SIRT1, 1.81 ± 0.10, n = 9) and Cdkn1b (HSV GFP, 1.00 ± 0.05, n = 9; vs HSV-SIRT1, 1.68 ± 0.06, n = 9). C, Western blotting of nuclear or cytosolic fractions of NAc of mice treated chronically with saline or cocaine reveals a significant increase in FOXO3a protein levels in nuclear fractions (HSV GFP, 1.00 ± 0.29, n = 7; vs HSV-SIRT1, 2.93 ± 0.38, n = 7), with no differences in cytosolic fractions. D, Chronic cocaine administration induces downstream FOXO3a targets in NAc: Gadd45α (saline, 1.00 ± 0.02, n = 8; vs cocaine, 1.426 ± 0.06, n = 9) and Cdkn1b (saline, 1.00 ± 0.032, n = 8; vs cocaine, 1.301 ± 0.06, n = 9). *p < 0.05.