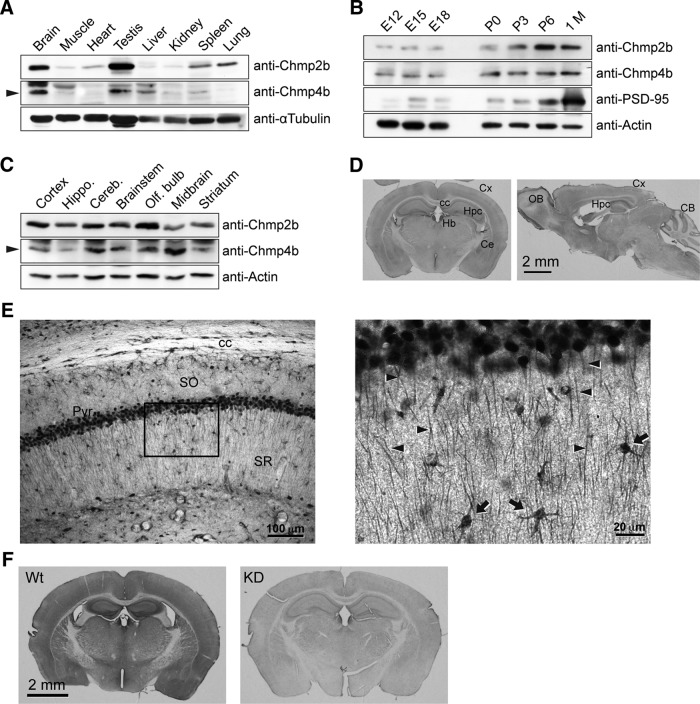
Figure 1.
Chmp2b expression in the mouse brain. A, An adult male mouse was dissected, and equal amounts of total protein from each tissue were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The arrowhead indicates the Chmp4b-specific band. α-Tubulin was used as the loading control. B, Mouse brains at increasing developmental ages were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. PSD-95 was used as a marker of synaptogenesis. P, Postnatal age (days); 1 M, 1 month. C, Equal protein amounts from the indicated regions of an adult mouse brain were analyzed by immunoblotting as above. D, Frontal (left) or sagittal (right) sections from adult mouse brain were stained by immunoperoxidase with anti-Chmp2b antibody. Cx, Cortex; cc, corpus callosum; Hpc, hippocampus; Hb, habenula; Ce, central amygdala; OB, olfactory bulb; CB, cerebellum. E, Left, Immunostained CA1 layer in a frontal section of the hippocampus. Note the strong staining of pyramidal cell bodies and the weaker but definite immunoreactivity of the neuropil. SO, Stratum oriens; Pyr, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum. Right, Higher magnification of the boxed region. Immunoreactivity is observed in apical dendrites (arrowheads) and interneurons (arrows). F, Specificity of Chmp2b immunostaining. As a control, we used brain sections from Chmp2b KO mice (Ghazi-Noori et al., 2012), here called Chmp2b KD because of the presence of residual Chmp2b protein in these mice (Fig. 7G,H). Chmp2b immunoreactivity was revealed by immunoperoxidase in a frontal section of the brain of a 5-week-old wild-type (Wt) mouse (left) or in an equivalent section of a sibling KD mouse (right). Note that development of DAB staining was performed identically for the two sections, but for a longer time than in D, which therefore appears lighter than F (Wt).