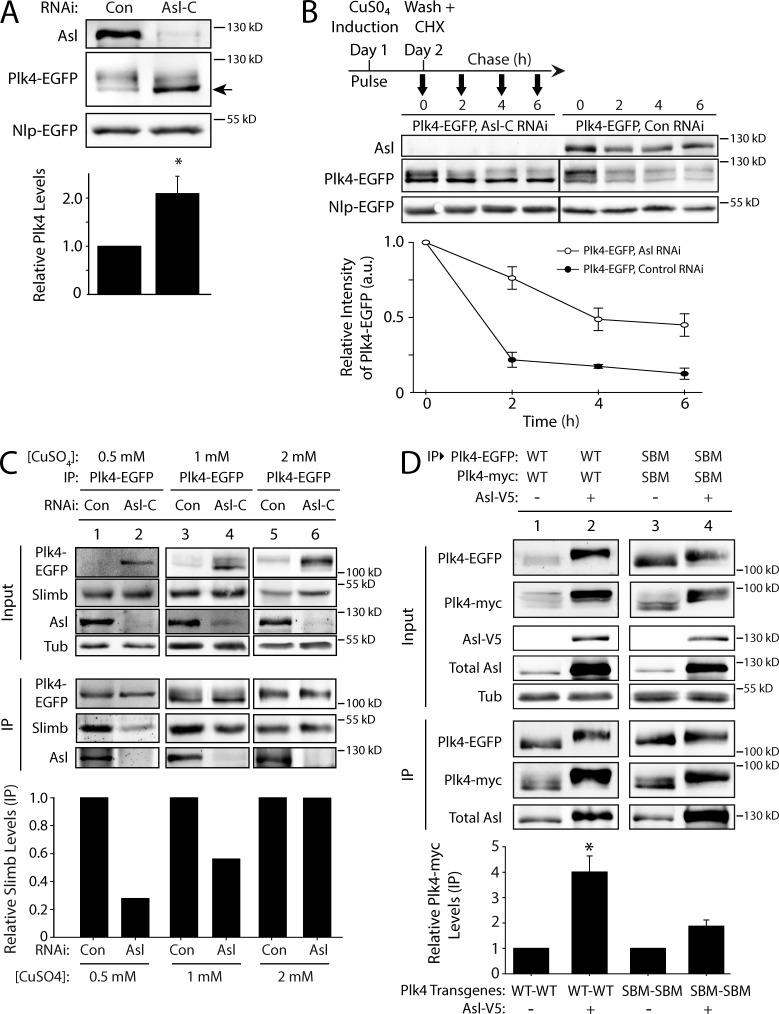
Figure 5.
Asl functions to promote Plk4 dimerization and autophosphorylation. (A) Asl increases the phosphorylation state of Plk4. S2 cells were control or Asl depleted for 5 d. On day 3, cells were transfected with Plk4-EGFP, and the next day, they were induced to express for 24 h. Immunoblots of cell lysates were probed for Asl and GFP. Cotransfected Nlp-EGFP was used as a loading control. Asl depletion increases the proportion of Plk4-EGFP with higher electrophoretic mobility (arrow), indicating decreased Plk4 phosphorylation. The graph shows relative amounts of Plk4-EGFP as determined by densitometry of the anti-GFP immunoblots, normalized to Nlp-EGFP, and plotted relative to control (lane 1). n = 6 experiments. (B) Plk4 turnover is suppressed in the absence of Asl. S2 cells were control or Asl depleted for 7 d. On day 5, cells were cotransfected with Plk4-EGFP and Nlp-EGFP (loading control) and induced the next day to express for 24 h. Cycloheximide (CHX) treatment was performed as indicated in the schematic and as described in Fig. 4 A. Immunoblots of cell lysates were probed for GFP and Asl. Plk4-EGFP protein levels were analyzed by densitometry of the anti-GFP immunoblots. Graphs show relative Plk4-EGFP levels for each treatment normalized against Nlp-EGFP for two experiments. (C) The impact of Asl on Plk4 autophosphorylation and Slimb binding can be masked by high levels of Plk4 expression. S2 cells were control or Asl-RNAi treated for 7 d. On day 5, cells were transfected with Plk4-EGFP, and the next day, they were induced to express using three different concentrations of CuSO4 for 24 h. Anti-GFP immunoprecipitates (IPs) were then prepared from lysates, and immunoblots were probed for GFP, Slimb, Asl, and α-tubulin. Graph shows relative amounts of Slimb as determined by densitometry of the anti-Slimb immunoblots, normalized to Plk4-EGFP. Data shown are from a single representative experiment (n = 2 independent experiments). (D) Asl increases Plk4 dimerization. Anti-GFP immunoprecipitates were prepared from lysates of S2 cells transiently coexpressing Plk4-EGFP and Plk4-myc and with or without Asl-V5. Blots of the input lysates and immunoprecipitates were probed for α-tubulin, GFP, V5, Asl, and myc. The graph shows relative amounts of Plk4-myc bound to Plk4-EGFP. For each treatment, levels of tagged Plk4 in the immunoprecipitates were determined by densitometry of the anti-GFP and myc immunoblots, normalized to measure Plk4-EGFP, and then plotted relative to control (lane 1). Asterisks mark significant difference compared with control. *, 0.05 > P ≥ 0.01. n = 3–4 experiments per treatment. Error bars indicate SEM. a.u., arbitrary unit; Con, control; Tub, tubulin.