Figure 5.
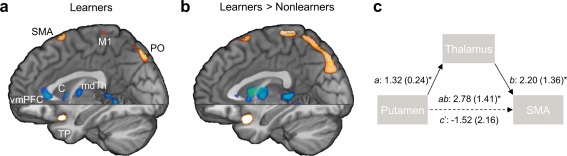
Learning‐related changes in connectivity with the posterolateral putamen (Q × posterolateral putamen PPI). (a) PPI map in learners. (b) Difference map for the PPI between learners and nonlearners. (c) Path diagram of intrinsic connections between the putamen and the premotor cortex‐SMA (SMA) via the thalamus supporting a full mediation effect in learners (path coefficients are shown [s.e. in parenthesis]; a: P = 10−6, b: P = 0.001, putamen‐SMA path c: P = 0.04, ab‐controlled putamen‐SMA path c′: P = 0.8, ab: P = 4 × 10−7, bootstrap test). C: caudate; M1: motor cortex; mdTh: mediodorsal thalamus; PO: parieto‐occipital region; SMA: supplementary motor area; TP: temporal pole; vmPFC: ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Note that spatial smoothing with a Gaussian kernel (full‐width‐at‐half‐maximum = 2 mm) was applied to reduce edge effects for visualization purposes. Supporting information Fig. S5 presents whole‐brain axial sections of the nonsmoothed difference map for PPI between learners and nonlearners.
