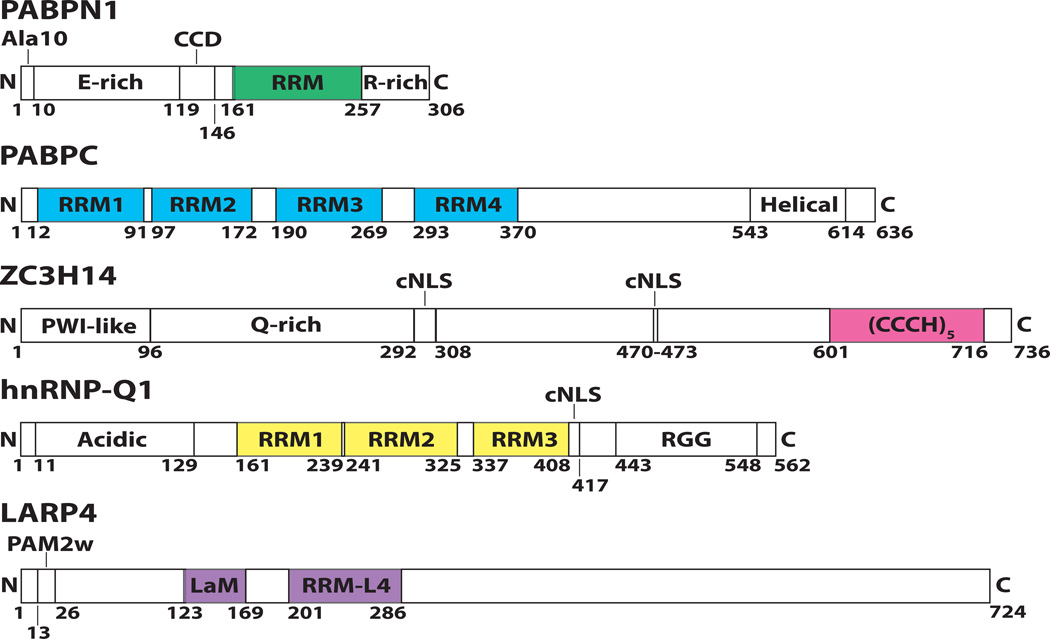
Figure 1. Pab protein domain structures and family members.
The domain structures for the five Pab family members discussed in this review (PABPN1, PABPC, ZC3H14, hnRNP-Q1, and LARP4) are schematized here. RNA binding modules are highlighted in colors that correspond with each of these proteins in subsequent figures. PABPN1 is a nuclear Pab that contains a stretch of 10 alanines (Ala10) that are expanded in OPMD, a glutamic acid-rich domain (E-rich), a coiled-coil domain (CCD), an RNA recognition motif (RRM) that is responsible for high affinity polyadenosine RNA binding, as well as an arginine-rich (R-rich) domain at the C-terminus. PABPC is a cytoplasmic Pab that interacts with polyadenosine RNA via RRMs (RRM1-4) and contains a C-terminal Helical domain. ZC3H14 is a novel nuclear Pab that interacts with polyadenosine RNA via tandem CysCysCysHis (CCCH) zinc fingers and also contains an N-terminal Proline Tryptophan Isoleucine-like (PWI-like) fold that mediates interactions with the nuclear pore, a glutamine-rich (Q-rich) domain of unknown function, and two putative classical nuclear localization signals (cNLS). hnRNP-Q1 is a novel cytoplasmic Pab that is presumed to bind polyadenosine RNA via RRMs (RRM1-3) and contains an Acidic N-terminal domain as well as an Arginine Glycine Glycine (RGG) domain, both of which mediate protein-protein interactions. A putative weak cNLS is also present in hnRNP-Q1. LARP4 is a novel cytoplasmic Pab that interacts with polyadenosine RNA via a La Motif (LaM) in conjunction with an RRM-like 4 domain (RRM-L4). LARP4 interacts with PABPC via a poly(A) binding protein interacting motif (PAM2) domain that contains an atypical tryptophan in the consensus sequence (PAM2w).