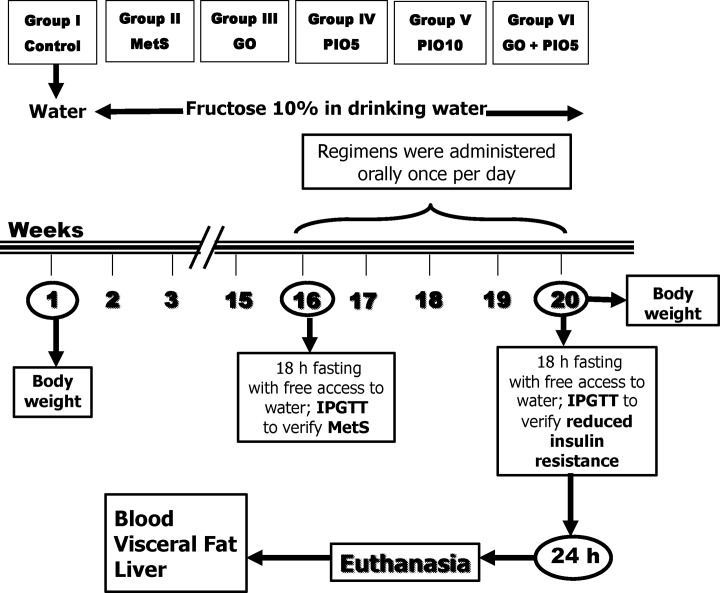
Fig 1. Adult male Wistar rats (45 days; 170±20 g) were randomly divided into 2 experimental subsets, namely, control group (free access to water for 16 weeks then vehicle for 4 weeks) or metabolic syndrome (MetS; 10% fructose solution in drinking water for 16 weeks) subset.
After 16 weeks, all animals were exposed to the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) after an overnight fast; and MetS was verified in the fructose fed rats. In the MetS experimental subset, rats were subdivided into MetS (1% Tween 80; 4 weeks; p.o), geraniol (GO; 250 mg/kg/day; 4 weeks; p.o); pioglitazone (PIO; 5 and 10 mg/kg/day; 4 weeks; p.o), and GO/PIO5 groups. These animals were further supplied with 10% fructose solution in drinking water for 4 weeks. Insulin resistance was tested using IPGTT 24 h after last treatments or vehicle administration and after an overnight fast in all groups. Body weight was recorded at baseline and after 20 weeks of the beginning of the experiments. Blood was collected and then rats were euthanized to dissect the liver and visceral fat for different assessments.