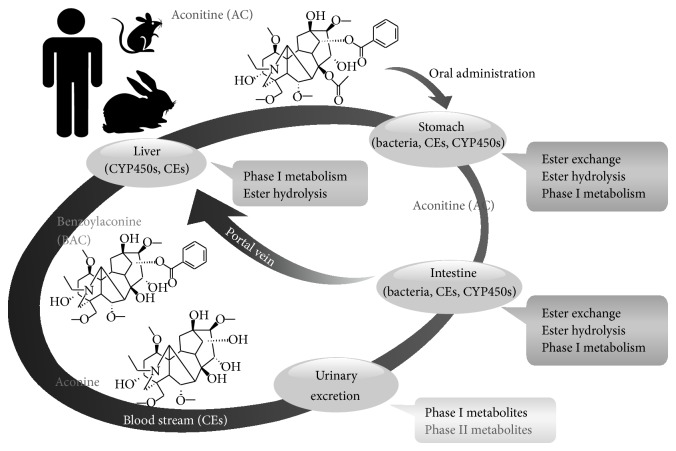
Figure 2.
The proposed process of toxicity reduction after oral AC administration in humans and experimental animals. The metabolites from ester exchange are lipo-alkaloids. Ester hydrolysis occurs at the C-8 or/and C-14 position, producing benzoylaconine (BAC) and aconine. Phase I metabolism refers to hydroxylation, deoxylation, dehydrogenation, demethylation, and didemethylation/deethylation. A few phase II metabolites were detected in the urine, including BAC glucuronide and AC sulfate conjugates. Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP450s), carboxylesterases (CEs), and enzymes produced by intestinal bacteria are involved in gastrointestinal and hepatic metabolism of aconitine (AC).