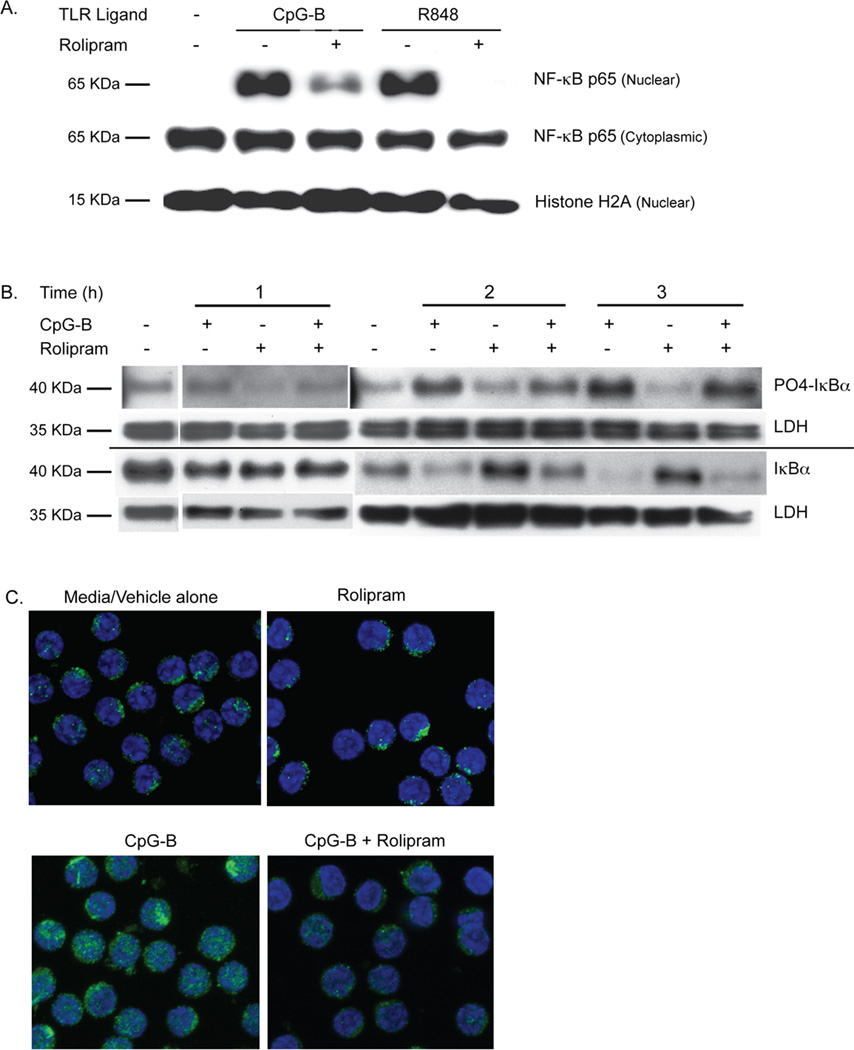
Figure 5.
PDE4 inhibitors block TLR7 and TLR9 ligand-induced NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation in CLL. (A) Leukemic cells from a CLL patient were incubated for two hours with media alone, the TLR9 agonist CpG-B (5 µg/mL) or the TLR7 agonist R848 (3 µg/mL) either with rolipram or without rolipram (20 µM). Proteins extracted from the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of these cells were then Western blotted for NF- κB p65 as well as the nuclear marker histone H2A. Blots are representative of eight CLL patients tested with CpG-B and three CLL patients tested with R848. (B) Leukemic cells from a CLL patient were incubated with vehicle alone or the TLR9 agonist CpG-B (5 µg/mL), rolipram (20 µM) or a combination of these two stimuli for 1, 2 or 3 hours. Cell lysates were assessed by Western analysis for levels of total or phosphorylated IκBα. The relative loading of cell lysates for each experimental sample was established by also determining levels of LDH on the same Western blot membrane. Blots are representative of five CLL patients tested. (C) The cytoplasmic or nuclear localization of NF-κB p65 in CLL cells was determined after two hours of incubation in media with vehicle alone, rolipram (20 µM), the TLR9 agonist CpG-B (5 µg/mL) or the combination of CpG-B and rolipram. NF-κB p65 was localized by immunohistochemical analysis of permeabilized CLL cells using a confocal fluorescent microscope. In these 100× images, p65 is labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 (green) and the nucleus is counterstained with TO-PRO-3 (blue). Images are representative of three patients tested. CT = Control.