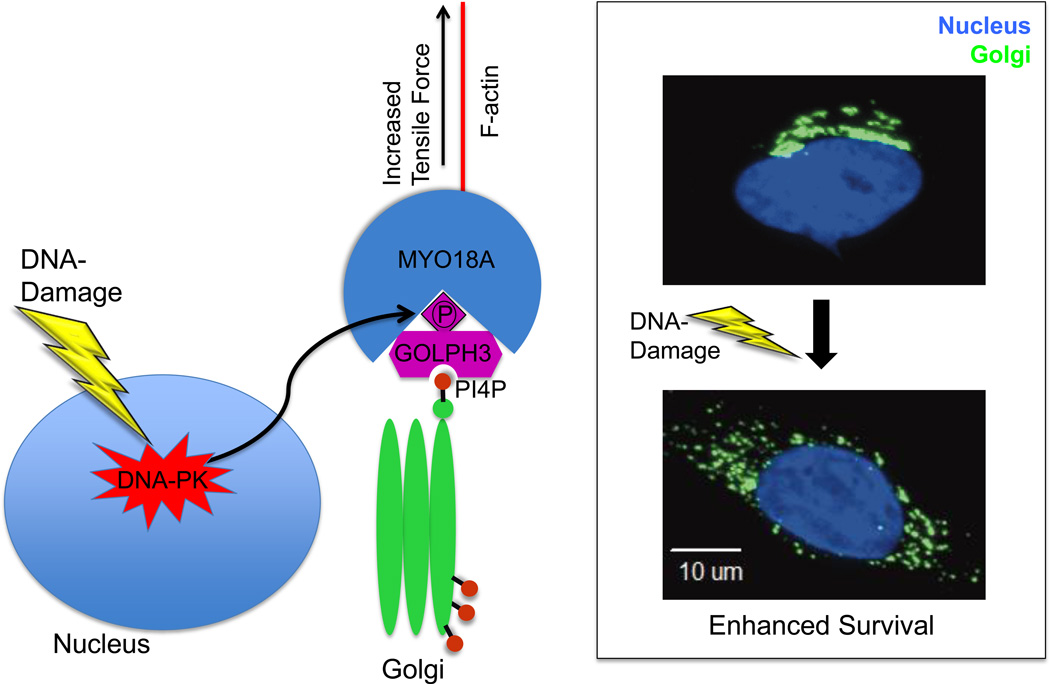
Figure.
Mechanism of DNA damage induced dispersal of the Golgi. In response to DNA damage, DNA-PK is activated and phosphorylates GOLPH3 on the T143 TQ motif. This phosphorylation results in increased GOLPH3 interaction with MYO18A and consequently an increased tensile force on the Golgi, leading to Golgi vesiculation, fragmentation, and dispersal. The DNA-PK/GOLPH3/MYO18A pathway is required for cell survival following DNA damage, and overexpression of GOLPH3 confers resistance to killing by DNA damaging agents.